Convalescent plasma donors show enhanced cross-reactive neutralizing antibody response to antigenic variants of SARS-CoV-2 following immunization
- PMID: 35588314
- PMCID: PMC9348319
- DOI: 10.1111/trf.16934
Convalescent plasma donors show enhanced cross-reactive neutralizing antibody response to antigenic variants of SARS-CoV-2 following immunization
Abstract
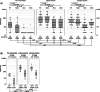
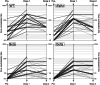
Background: The therapeutic benefit of convalescent plasma (CP) therapy to treat COVID-19 may derive from neutralizing antibodies (nAbs) to SARS-CoV-2. To investigate the effects of antigenic variation on neutralization potency of CP, we compared nAb titers against prototype and recently emerging strains of SARS-CoV-2, including Delta and Omicron, in CP donors previously infected with SARS-CoV-2 before and after immunization.
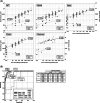
Methods and materials: Samples were assayed from previously SARS-CoV-2 infected donors before (n = 17) and after one (n = 43) or two (n = 71) doses of Astra-Zeneca or Pfizer vaccinations. Ab titers against Wuhan/wild type (WT), Alpha, Beta, and Delta SARS-CoV-2 strains were determined by live virus microneutralization assay while titers to Omicron used a focus reduction neutralization test. Anti-spike antibody was assayed by Elecsys anti-SARS-CoV-2 quantitative spike assay (Roche).
Results: Unvaccinated donors showed a geometric mean titer (GMT) of 148 against WT, 80 against Alpha but mostly failed to neutralize Beta, Delta, and Omicron strains. Contrastingly, high GMTs were observed in vaccinated donors against all SARS-CoV-2 strains after one vaccine dose (WT:703; Alpha:692; Beta:187; Delta:215; Omicron:434). By ROC analysis, reactivity in the Roche quantitative Elecsys spike assay of 20,000 U/mL was highly predictive of donations with nAb titers of ≥1:640 against Delta (90% sensitivity; 97% specificity) and ≥1:320 against Omicron (89% sensitivity; 81% specificity).
Discussion: Vaccination of previously infected CP donors induced high levels of broadly neutralizing antibodies against circulating antigenic variants of SARS-CoV-2. High titer donations could be reliably identified by automated quantitative anti-spike antibody assay, enabling large-scale preselection of high-titer convalescent plasma.
Keywords: COVID-19; Delta; Omicron; SARS-CoV-2; antibody neutralization; antigenic variants; convalescent plasma; vaccination.
© 2022 The Authors. Transfusion published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of AABB.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organisation . Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS‐CoV‐2 variant of concern [monograph on the internet]. 2021. Available from: https://www.who.int/news/item/26-11-2021-classification-of-omicron-(b.1....
-
- Liu L, Iketani S, Guo Y, Chan JF, Wang M, Liu L, et al. Striking antibody evasion manifested by the omicron variant of SARS‐CoV‐2. Nature. 2021;602:676–81. - PubMed
-
- Planas D, Saunders N, Maes P, Guivel‐Benhassine F, Planchais C, Buchrieser J, et al. Considerable escape of SARS‐CoV‐2 Omicron to antibody neutralization. Nature. 2022;692:671–5. - PubMed
-
- Wilhelm A, Widera M, Grikscheit K, Toptan T, Schenk B, Pallas C, et al. Reduced neutralization of SARS‐CoV‐2 Omicron variant by vaccine sera and monoclonal antibodies. medRxiv. posted December 8, 2021. 12.07.21267432.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

