Highly prevalent MDR, frequently carrying virulence genes and antimicrobial resistance genes in Salmonella enterica serovar 4,[5],12:i:- isolates from Guizhou Province, China
- PMID: 35588421
- PMCID: PMC9119451
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266443
Highly prevalent MDR, frequently carrying virulence genes and antimicrobial resistance genes in Salmonella enterica serovar 4,[5],12:i:- isolates from Guizhou Province, China
Abstract
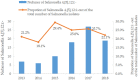
Salmonella enterica serovar 4,[5],12:i:-, a monophasic variant of Salmonella Typhimurium lacking the phase 2 flagellin, is one of the common serotypes causing Salmonellosis worldwide. However, information on Salmonella serovar 4,[5],12:i:- from Guizhou Province has lacked so far. This study aimed to investigate the antimicrobial resistance, the presence of antimicrobial resistance genes and virulence genes, and characterize the MLST genotypes of Salmonella serovar 4,[5],12:i:- isolates from Guizhou province, China. We collected 363 non-typhoid Salmonella (NTS) isolates of Guizhou from 2013 to 2018. Biochemical identification, serogroups testing, and specific multiplex polymerase chain reaction (mPCR) assay were conducted to identify Salmonella 4,[5],12:i:- isolates. Isolates were determined the antimicrobial resistance by the micro broth dilution method, detected the presence of antimicrobial resistance genes and virulence genes by PCR, and examined the molecular genotyping by Multilocus sequence typing (MLST). Eighty-seven Salmonella 4,[5],12:i:- isolates were detected, accounting for 23.9% (87/363) of the total NTS isolates. All Salmonella 4,[5],12:i:- isolates showed highly resistant to sulfaoxazole (93.1%), streptomycin (90.8%), ampicillin (88.5%), tetracycline (86.2%) and doxycycline (86.2%). A high proportion (94.2%) of multi-drug resistance (MDR) isolates were found. Most (83.9%) Salmonella 4,[5],12:i:- isolates carried four antimicrobial resistance genes, especially blaTEM-1, strA-strB, sul2, and tetB genes. Salmonella 4,[5],12:i:- isolates showed a high rate of invA, sseL, mgtC, siiE, sopB, gipA, gtgB, sspH1, and sspH2 (72.4%~98.9%). On the contrary, none of the isolates were detected the spvC and pefA genes. MLST analysis revealed three sequence types (STs), and ST34 (97.7%) was the dominant sequence type. This study is the first report of Salmonella 4,[5],12:i:- in humans from Guizhou province, China. The data might be useful for rational antimicrobial usage against Salmonella 4,[5],12:i:- infections, risk management, and public health strategies in Guizhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and Characterization of Monophasic Salmonella Serovar 1,4,[5],12:i:- of Food Origin in China.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 11;10(9):e0137967. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137967. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26360603 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Based Assessment of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Potential of Isolates of Non-Pullorum/Gallinarum Salmonella Serovars Recovered from Dead Poultry in China.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0096522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00965-22. Epub 2022 Jun 21. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35727054 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Human Origin Salmonella Serovar 1,4,[5],12:i:- in Eastern China, 2014 to 2018.Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2021 Nov;18(11):790-797. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2021.0008. Epub 2021 Jul 20. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2021. PMID: 34287022
-
Drug resistance and virulence-associated genes screening in Salmonella enterica isolated from Caspian pony, Iran.Vet Res Forum. 2024;15(9):481-486. doi: 10.30466/vrf.2024.2014684.4051. Epub 2024 Sep 15. Vet Res Forum. 2024. PMID: 39564468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxin-Antitoxin Systems: A Key Role on Persister Formation in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium.Infect Drug Resist. 2022 Oct 3;15:5813-5829. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S378157. eCollection 2022. Infect Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 36213766 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Virulence potential of Salmonella 1,4, [5],12:i:- strains isolated during decades from different sources in the Southeast region of Brazil.Braz J Microbiol. 2023 Dec;54(4):2827-2843. doi: 10.1007/s42770-023-01145-5. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Braz J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37817050 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial resistance and genomic investigation of Salmonella isolated from retail foods in Guizhou, China.Front Microbiol. 2024 Mar 6;15:1345045. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1345045. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38510999 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome sequencing of Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates from a tertiary hospital in Terengganu, Malaysia (2011-2020), revealed the predominance of the Global Clone 2 lineage.Microb Genom. 2025 Feb;11(2):001345. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.001345. Microb Genom. 2025. PMID: 39908088 Free PMC article.
-
Serovar and sequence type distribution and phenotypic and genotypic antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella originating from pet animals in Chongqing, China.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jul 2;12(7):e0354223. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03542-23. Epub 2024 May 17. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38757951 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance Diversity of Salmonella Isolates in Jiaxing City, China.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 May 14;13(5):443. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13050443. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38786171 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lettini AA, Saccardin C, Ramon E, Longo A, Cortini E, Dalla Pozza MC, et al.. Characterization of an unusual Salmonella phage type DT7a and report of a foodborne outbreak of salmonellosis. Int J Food Microbiol. 2014; 189: 11–17. Epub 2014/08/12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2014.07.021 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources