Estimating the threshold of health workforce densities towards universal health coverage in Africa
- PMID: 35589142
- PMCID: PMC9109029
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjgh-2021-008310
Estimating the threshold of health workforce densities towards universal health coverage in Africa
Abstract
Background: There have been past efforts to develop benchmarks for health workforce (HWF) needs across countries which have been helpful for advocacy and planning. Still, they have neither been country-specific nor disaggregated by cadre-primarily due to data inadequacies. This paper presents an analysis to estimate a threshold of 13 cadres of HWF density to support the progressive realisation of universal health coverage (UHC).
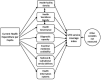
Method: Using UHC service coverage as the outcome measure, a two-level structural equation model was specified and analysed in STATA V.16. In the first level of structural equations, health expenditure per capita-one of the cross-cutting inputs for UHC, was used to explain the critical inputs for service delivery/coverage. In the second level of the model, the critical inputs for service delivery were used to explain the UHC Service Coverage Index (UHC SCI), in which the contribution of the HWF was 'partial out'.
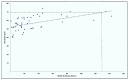
Results: The analysis found that a unit increase in the HWF density per 10 000 population is positively associated with statistically significant improvements in the UHC SCI of countries (β=0.127, p<0.001). Similarly, a positive and statistically significant association was established between diagnostic readiness and the UHC SCI (β=0.243, p=0.015). Essential medicines readiness was positively correlated but not statistically significant (β=0.053, p=0.658). Controlling for other variables, a density of 134.23 per 10 000 population across 13 HWF categories is necessary to attain at least 70% UHC SCI.
Conclusion: Consistent with current knowledge, the HWF is a significant predictor of the UHC SCI. Attaining at least 70% of the UHC SCI requires about 134.23 health workers (a mix of 13 cadres) per 10 000 population.
Keywords: Africa; HRH planning; Health workforce density; Human Resources for Health; Reduced Gradient (GRG) approach; Threshold density; Universal Health Coverage (UHC) service index; structural equation model.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- ILO . World social protection report 2014/15. Geneva, Switzerland: International Labour Organisation, 2014. https://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:8bm9qdHvrCMJ:https...
-
- World Health Organization . Global strategy on human resources for health: workforce 2030. World health organisation published online first, 2016. Available: https://www.who.int/hrh/resources/globstrathrh-2030/en/
-
- World Health Organization . The world health report: 2006: working together for health. published online first, 2006. Available: http://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/43432 [Accessed 10 Oct 2016].
-
- World Health Organization . Health workforce requirements for universal health coverage and the Sustainable Development Goals.(Human Resources for Health Observer, 17). Human Resources for Health Observer Series No 17 2016;17:40.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous