The ubiquitin ligase Cul5 regulates CD4+ T cell fate choice and allergic inflammation
- PMID: 35589717
- PMCID: PMC9120070
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30437-x
The ubiquitin ligase Cul5 regulates CD4+ T cell fate choice and allergic inflammation
Abstract
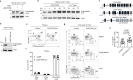
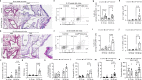
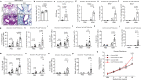
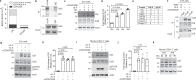
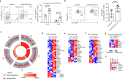
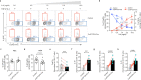
Antigen encounter directs CD4+ T cells to differentiate into T helper or regulatory cells. This process focuses the immune response on the invading pathogen and limits tissue damage. Mechanisms that govern T helper cell versus T regulatory cell fate remain poorly understood. Here, we show that the E3 ubiquitin ligase Cul5 determines fate selection in CD4+ T cells by regulating IL-4 receptor signaling. Mice lacking Cul5 in T cells develop Th2 and Th9 inflammation and show pathophysiological features of atopic asthma. Following T cell activation, Cul5 forms a complex with CIS and pJak1. Cul5 deletion reduces ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of pJak1, leading to an increase in pJak1 and pSTAT6 levels and reducing the threshold of IL-4 receptor signaling. As a consequence, Cul5 deficient CD4+ T cells deviate from Treg to Th9 differentiation in low IL-4 conditions. These data support the notion that Cul5 promotes a tolerogenic T cell fate choice and reduces susceptibility to allergic asthma.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epimedin C modulates the balance between Th9 cells and Treg cells through negative regulation of noncanonical NF-κB pathway and MAPKs activation to inhibit airway inflammation in the ovalbumin-induced murine asthma model.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Dec;65:102005. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2021.102005. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 33636365
-
The CUL5 E3 ligase complex negatively regulates central signaling pathways in CD8+ T cells.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 19;15(1):603. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44885-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38242867 Free PMC article.
-
B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein 1 controls TH9 cell development, IL-9 production, and allergic inflammation.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 Mar;143(3):1119-1130.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.06.046. Epub 2018 Aug 7. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30096391 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Roles of Balanced T Helper 9 Cells and Regulatory T Cells in Allergic Airway Inflammation and Tumor Immunity.J Immunol Res. 2021 Mar 1;2021:8816055. doi: 10.1155/2021/8816055. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 33748292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Th9 and other IL-9-producing cells in allergic asthma.Semin Immunopathol. 2017 Jan;39(1):55-68. doi: 10.1007/s00281-016-0601-1. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Semin Immunopathol. 2017. PMID: 27858144 Review.
Cited by
-
How GRAIL controls Treg function to maintain self-tolerance.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 8;13:1046631. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1046631. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36569931 Free PMC article.
-
BAP31 Knockout in Macrophages Affects CD4+T Cell Activation through Upregulation of MHC Class II Molecule.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 30;24(17):13476. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713476. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686286 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin proteasome system in immune regulation and therapeutics.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2022 Dec;67:102310. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2022.102310. Epub 2022 Oct 23. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36288660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PSMC2 is a Novel Prognostic Biomarker and Predicts Immunotherapeutic Responses: From Pancreatic Cancer to Pan-Cancer.Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2023 Aug 9;16:747-758. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S418533. eCollection 2023. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37581119 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Regions Associated with Resistance to Gastrointestinal Nematode Parasites in Sheep-A Review.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jan 30;15(2):187. doi: 10.3390/genes15020187. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397178 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

