Microfluidic-assisted synthesis and modeling of stimuli-responsive monodispersed chitosan microgels for drug delivery applications
- PMID: 35589742
- PMCID: PMC9120176
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-12031-9
Microfluidic-assisted synthesis and modeling of stimuli-responsive monodispersed chitosan microgels for drug delivery applications
Abstract
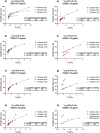
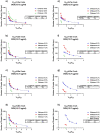
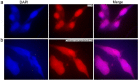
Droplet microfluidic has been established to synthesize and functionalize micro/nanoparticles for drug delivery and screening, biosensing, cell/tissue engineering, lab-on-a-chip, and organ-on-a-chip have attracted much attention in chemical and biomedical engineering. Chitosan (CS) has been suggested for different biomedical applications due to its unique characteristics, such as antibacterial bioactivities, immune-enhancing influences, and anticancer bioactivities. The simulation results exhibited an alternative for attaining visions in this complex method. In this regard, the role of the flow rate ratio on the CS droplet features, including the generation rate and droplet size, were thoroughly described. Based on the results, an appropriate protocol was advanced for controlling the CS droplet properties for comparing their properties, such as the rate and size of the CS droplets in the microchip. Also, a level set (LS) laminar two-phase flow system was utilized to study the CS droplet-breaking process in the Flow Focused-based microchip. The outcomes demonstrated that different sizes and geometries of CS droplets could be established via varying the several parameters that validated addressing the different challenges for several purposes like drug delivery (the droplets with smaller sizes), tissue engineering, and cell encapsulation (the droplets with larger sizes), lab-on-a-chip, organ-on-a-chip, biosensing and bioimaging (the droplets with different sizes). An experimental study was added to confirm the simulation results. A drug delivery application was established to verify the claim.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
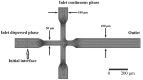
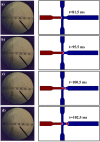

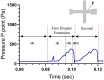
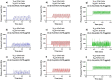


References
-
- Rahimzadeh Z, et al. A rapid nanobiosensing platform based on herceptin-conjugated graphene for ultrasensitive detection of circulating tumor cells in early breast cancer. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2021;10:744–753. doi: 10.1515/ntrev-2021-0049. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

