Comprehensive genome analysis of Lentzea reveals repertoire of polymer-degrading enzymes and bioactive compounds with clinical relevance
- PMID: 35589875
- PMCID: PMC9120177
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-12427-7
Comprehensive genome analysis of Lentzea reveals repertoire of polymer-degrading enzymes and bioactive compounds with clinical relevance
Abstract
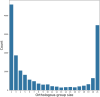
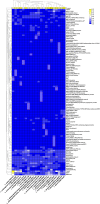
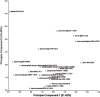
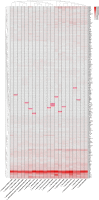
The genus Lentzea is a rare group of actinobacteria having potential for the exploration of bioactive compounds. Despite its proven ability to produce compounds with medical relevance, Lentzea genome analysis remains unexplored. Here we show a detailed understanding of the genetic features, biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs), and genetic clusters for carbohydrate-active enzymes present in the Lentzea genome. Our analysis determines the genes for core proteins, non-ribosomal peptide synthetase condensation domain, and polyketide synthases-ketide synthase domain. The antiSMASH-based sequence analysis identifies 692 BGCs among which 8% are identical to the BGCs that produce geosmin, citrulassin, achromosin (lassopeptide), vancosamine, anabaenopeptin NZ857/nostamide A, alkylresorcinol, BE-54017, and bezastatin. The remaining BGCs code for advanced category antimicrobials like calcium-dependent, glycosylated, terpenoids, lipopeptides, thiopeptide, lanthipeptide, lassopeptide, lingual antimicrobial peptide and lantibiotics together with antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal, antiparasitic, anticancer agents. About 28% of the BGCs, that codes for bioactive secondary metabolites, are exclusive in Lentzea and could lead to new compound discoveries. We also find 7121 genes that code for carbohydrate-degrading enzymes which could essentially convert a wide range of polymeric carbohydrates. Genome mining of such genus is very much useful to give scientific leads for experimental validation in the discovery of new-generation bioactive molecules of biotechnological importance.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Biosynthetic gene clusters with biotechnological applications in novel Antarctic isolates from Actinomycetota.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 May 8;108(1):325. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13154-x. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38717668 Free PMC article.
-
Colibrimycins, Novel Halogenated Hybrid Polyketide Synthase-Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetase (PKS-NRPS) Compounds Produced by Streptomyces sp. Strain CS147.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Jan 11;88(1):e0183921. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01839-21. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34669429 Free PMC article.
-
Draft genome and secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters of Streptomyces sp. strain 196.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Sep;47(9):6741-6747. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05731-w. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32888130
-
An Overview on Nocardiopsis Species Originating From North African Biotopes as a Promising Source of Bioactive Compounds and In Silico Genome Mining Analysis of Three Sequenced Genomes.J Basic Microbiol. 2024 Sep;64(9):e2400046. doi: 10.1002/jobm.202400046. Epub 2024 Jun 27. J Basic Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38934516 Review.
-
Challenges of functional expression of complex polyketide biosynthetic gene clusters.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2021 Jun;69:103-111. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2020.12.007. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33422913 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of Lentzea flaviverrucosa strain E25-2 isolated from Moroccan forest soil.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jul 22;15:1429035. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1429035. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39104582 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic and structural response of a multispecies biofilm to environmental perturbations induced by the continuous increase of benzimidazole fungicides in a permeable reactive biobarrier.J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2024 May 7;22(1):329-344. doi: 10.1007/s40201-024-00903-3. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2024. PMID: 38887762 Free PMC article.
-
Luteibacter sahnii sp. nov., A Novel Yellow-Colored Xanthomonadin Pigment Producing Probiotic Bacterium from Healthy Rice Seed Microbiome.Curr Microbiol. 2024 Oct 24;81(12):424. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-03950-z. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39446145
-
Variability of microbiomes in winter rye, wheat, and triticale affected by snow mold: predicting promising microorganisms for the disease control.Environ Microbiome. 2025 Jan 11;20(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s40793-025-00665-x. Environ Microbiome. 2025. PMID: 39799378 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a Novel Lentzea Species Isolated from the Kumtagh Desert and Genomic Insights into the Secondary Metabolite Potential of the Genus.Microorganisms. 2025 Jul 10;13(7):1628. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13071628. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40732136 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

