Modified os sepiae of Sepiella inermis as a low cost, sustainable, bio-based adsorbent for the effective remediation of boron from aqueous solution
- PMID: 35589901
- PMCID: PMC9515050
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-022-20578-3
Modified os sepiae of Sepiella inermis as a low cost, sustainable, bio-based adsorbent for the effective remediation of boron from aqueous solution
Abstract
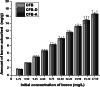
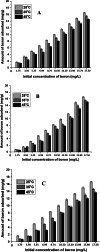
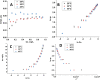
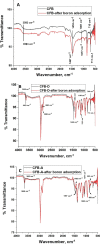
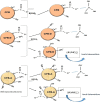
The occurrence of boron in low concentration is essential; however, a higher concentration of boron source in water has a toxic effect on humans as well as have retard effect on agricultural plant growth. Thus, the affordable and facile method to remediate water from higher boron concentrations is highly demanded. This report explores the ability of naturally occurring sustainable bio-waste os sepiae (cuttlefish bone, CFB) as an effective adsorbent for the removal of boron from water. Chemical activation of the os sepiae powder was examined to improve the efficiency of boron adsorption. A batch adsorption study for boron considering various parameters such as chemical modification of os sepiae, pH, initial boron concentration, and the temperature was scrutinized. Untreated (CFB), alkali-treated (CFB-D) and acid-treated (CFB-A) os sepiae powders were investigated and the adsorption capacities reached up to 53.8 ± 0.04 mg/g, 66.4 ± 0.02 mg/g and 69.8 ± 0.02 mg/g, respectively, at optimal pH 8 and 25 °C. Boron adsorption by CFB, CFB-D, and CFB-A were well fitted with the linear Freundlich adsorption isotherm model with a correlation coefficient of 99.4%, 99.8%, and 99.7% respectively. Thermodynamic parameters indicated that the adsorption of boron by CFB is an exothermic process and more feasible at a lower temperature around 25 °C. Moreover, detailed morphological and chemical characterization of the influence of adsorbed boron on adsorbents was conducted and discussed. The Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis spectra confirms the involvement of various functional groups including amino, carbonate (CO3)2-, and hydroxyl groups on the adsorbent in the adsorption mechanisms for boron removal. The results indicate that CFB can be an excellent example for the recycling and reuse of biowaste for water remediation.
Keywords: Adsorption; Boron; Os sepiae; Upcycling; Water treatment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

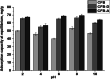





References
-
- Abdel-Khalek MA, Rahman MA, Francis AA. Exploring the adsorption behavior of cationic and anionic dyes on industrial waste shells of egg. J Environ Chem Eng. 2017;5(1):319–327. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2016.11.043. - DOI
-
- Abdul Rahman A (2014) KAHRAMAA Drinking Water Quality Requirements. https://www.km.com.qa/MediaCenter/Publications/KAHRAMAA/20Drinking/20Wat.... Accessed 22 Oct 2021
-
- Ahmad R, Kumar R, Haseeb S. Adsorption of Cu2+ from aqueous solution onto iron oxide coated eggshell powder: Evaluation of equilibrium, isotherms, kinetics, and regeneration capacity. Arab J Chem. 2012;5(3):353–359. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2010.09.003. - DOI
-
- Ahmed FE, Khalil A, Hilal N. Emerging desalination technologies: Current status, challenges and future trends. Desalination. 2021;517:115183. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2021.115183. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

