Prevalence of pain in community-dwelling older adults with hypertension in the United States
- PMID: 35589916
- PMCID: PMC9119929
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-12331-0
Prevalence of pain in community-dwelling older adults with hypertension in the United States
Abstract
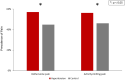
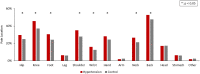
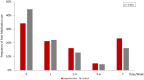
Hypertension and pain are both prevalent conditions in the older adult population. We aimed to report the prevalence of pain discomforts and investigated the association between hypertension and pain discomforts among older adults in the United States. Data from the 2011 National Health and Aging Trends Study were analyzed. In-person interviews were conducted in 7601 adults ages ≥ 65 years. Prevalence of bothersome pain, activity-limiting pain, locations of pain and usage of pain medicine were evaluated. Demographics, comorbidities, and other covariates were compared between older adults with hypertension and those without. Multivariate regression was further performed to yield adjusted odd ratios. Among 6825 older adults, 4533 of them had a history of hypertension while 2272 of them had not. Prevalence of bothersome pain (57.12% versus 44.81%, p < 0.001) and activity-limiting pain (56.21% versus 46.12%, p < 0.001) were significantly higher in the hypertension group. After adjusting for all covariates, hypertension demonstrated a significant association with activity-limiting pain (OR 1.63, 95% CI 1.06 to 2.52, p = 0.02). In conclusion, pain was more prevalent in older Americans with hypertension. The positive association between hypertension and pain suggested that routine pain assessment and proper treatment would be required to improve the function and quality of life among older adults especially with hypertension.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pain in Community-Dwelling Older Adults with Dementia: Results from the National Health and Aging Trends Study.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015 Aug;63(8):1503-11. doi: 10.1111/jgs.13536. Epub 2015 Jul 22. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015. PMID: 26200445 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal Patterns of Pain Reporting Among Community-dwelling Older Adults.Clin J Pain. 2020 Dec;36(12):912-922. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0000000000000874. Clin J Pain. 2020. PMID: 32841970
-
Prevalence and impact of pain among older adults in the United States: findings from the 2011 National Health and Aging Trends Study.Pain. 2013 Dec;154(12):2649-2657. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.07.029. Pain. 2013. PMID: 24287107 Free PMC article.
-
Symptom Burden Among Community-Dwelling Older Adults in the United States.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019 Feb;67(2):223-231. doi: 10.1111/jgs.15673. Epub 2018 Dec 12. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019. PMID: 30548453 Free PMC article.
-
The Coexistence of Hypertension and Arthritis Was Not Associated with Pain Severity in Community-Dwelling Older Adults in the United States.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Mar 6;13(5):570. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13050570. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40077132 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Longitudinal association between frailty and pain in three prospective cohorts of older population.J Nutr Health Aging. 2025 Jun;29(6):100537. doi: 10.1016/j.jnha.2025.100537. Epub 2025 Mar 23. J Nutr Health Aging. 2025. PMID: 40121961 Free PMC article.
-
A multi-ancestry genetic study of pain intensity in 598,339 veterans.Nat Med. 2024 Apr;30(4):1075-1084. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-02839-5. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Nat Med. 2024. PMID: 38429522 Free PMC article.
-
Rehabilitation management of the chronic pain-hypertension synergy: Proposal of an evidence-informed framework.Braz J Phys Ther. 2025 Jun 3;29(5):101229. doi: 10.1016/j.bjpt.2025.101229. Online ahead of print. Braz J Phys Ther. 2025. PMID: 40466275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of the WHO analgesic ladder on pain severity, pain interference, and blood pressure control in hypertensive patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain: a cross-sectional study.Prim Health Care Res Dev. 2024 Oct 14;25:e43. doi: 10.1017/S1463423624000367. Prim Health Care Res Dev. 2024. PMID: 39397485 Free PMC article.
-
Hypertension-Mediated Organ Damage in Relation to Severity of Chronic Low Back Pain in Hypertensive Patients.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024 Aug 28;11(9):266. doi: 10.3390/jcdd11090266. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024. PMID: 39330324 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ostchega, Y., Fryar, C. D., Nwankwo, T. & Nguyen, D. T. Hypertension prevalence among adults aged 18 and over: United States, 2017–2018. NCHS Data Brief 1–8 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

