Performance of PROPELLER FSE T2WI in reducing metal artifacts of material porcelain fused to metal crown: a clinical preliminary study
- PMID: 35589945
- PMCID: PMC9120134
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-12402-2
Performance of PROPELLER FSE T2WI in reducing metal artifacts of material porcelain fused to metal crown: a clinical preliminary study
Abstract
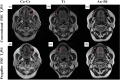
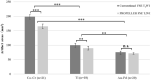
This study aimed to compare MRI quality between conventional fast spin echo T2 weighted imaging (FSE T2WI) with periodically rotated overlapping parallel lines with enhanced reconstruction (PROPELLER) FSE T2WI for patients with various porcelain fused to metal (PFM) crown and analyze the value of PROPELLER technique in reducing metal artifacts. Conventional FSE T2WI and PROPELLER FSE T2WI sequences for axial imaging of head were applied in participants with different PFM crowns: cobalt-chromium (Co-Cr) alloy, pure titanium (Ti), gold-palladium (Au-Pd) alloy. Two radiologists evaluated overall image quality of section in PFM using a 5-point scale qualitatively and measured the maximum artifact area and artifact signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) quantitatively. Fifty-nine participants were evaluated. The metal crown with the least artifacts and the optimum image quality shown in conventional FSE T2WI and PROPELLER FSE T2WI were in Au-Pd alloy, Ti, and Co-Cr alloy order. PROPELLER FSE T2WI was superior to conventional FSE T2WI in improving image quality and reducing artifact area for Co-Cr alloy (17.0 ± 0.2% smaller artifact area, p < 0.001) and Ti (11.6 ± 0.7% smaller artifact area, p = 0.005), but had similar performance compared to FSE T2WI for Au-Pd alloy. The SNRs of the tongue and masseter muscle were significantly higher on PROPELLER FSE T2WI compared with conventional FSE T2WI (tongue: 29.76 ± 8.45 vs. 21.54 ± 9.31, p = 0.007; masseter muscle: 19.11 ± 8.24 vs. 15.26 ± 6.08, p = 0.016). Therefore, the different PFM crown generate varying degrees of metal artifacts in MRI, and the PROPELLER can effectively reduce metal artifacts especially in the PFM crown of Co-Cr alloy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

