Absence of increased genomic variants in the cyanobacterium Chroococcidiopsis exposed to Mars-like conditions outside the space station
- PMID: 35589950
- PMCID: PMC9120168
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-12631-5
Absence of increased genomic variants in the cyanobacterium Chroococcidiopsis exposed to Mars-like conditions outside the space station
Abstract
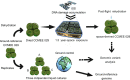
Despite the increasing interest in using microbial-based technologies to support human space exploration, many unknowns remain not only on bioprocesses but also on microbial survivability and genetic stability under non-Earth conditions. Here the desert cyanobacterium Chroococcidiopsis sp. CCMEE 029 was investigated for robustness of the repair capability of DNA lesions accumulated under Mars-like conditions (UV radiation and atmosphere) simulated in low Earth orbit using the EXPOSE-R2 facility installed outside the International Space Station. Genomic alterations were determined in a space-derivate of Chroococcidiopsis sp. CCMEE 029 obtained upon reactivation on Earth of the space-exposed cells. Comparative analysis of whole-genome sequences showed no increased variant numbers in the space-derivate compared to triplicates of the reference strain maintained on the ground. This result advanced cyanobacteria-based technologies to support human space exploration.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dried Biofilms of Desert Strains of Chroococcidiopsis Survived Prolonged Exposure to Space and Mars-like Conditions in Low Earth Orbit.Astrobiology. 2019 Aug;19(8):1008-1017. doi: 10.1089/ast.2018.1900. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Astrobiology. 2019. PMID: 30741568
-
Preservation of Biomarkers from Cyanobacteria Mixed with Mars-Like Regolith Under Simulated Martian Atmosphere and UV Flux.Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2016 Jun;46(2-3):289-310. doi: 10.1007/s11084-015-9467-9. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2016. PMID: 26530341
-
Biofilm and planktonic lifestyles differently support the resistance of the desert cyanobacterium Chroococcidiopsis under space and Martian simulations.Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2013 Oct;43(4-5):377-89. doi: 10.1007/s11084-013-9341-6. Epub 2013 Aug 18. Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2013. PMID: 23955666
-
Growing crops for space explorers on the moon, Mars, or in space.Adv Space Biol Med. 1999;7:131-62. doi: 10.1016/s1569-2574(08)60009-x. Adv Space Biol Med. 1999. PMID: 10660775 Review.
-
Radiation: microbial evolution, ecology, and relevance to mars missions.Mutat Res. 1999 Dec 6;430(2):281-91. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(99)00140-2. Mutat Res. 1999. PMID: 10631343 Review.
Cited by
-
First characterization of cultivable extremophile Chroococcidiopsis isolates from a solar panel.Front Microbiol. 2023 Feb 17;14:982422. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.982422. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36876112 Free PMC article.
-
Enabling deep-space experimentations on cyanobacteria by monitoring cell division resumption in dried Chroococcidiopsis sp. 029 with accumulated DNA damage.Front Microbiol. 2023 May 17;14:1150224. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1150224. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37266021 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen evolution from extremophilic cyanobacteria confined in hard biocoatings.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Sep 25;11(5):e0187023. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01870-23. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37747195 Free PMC article.
-
Extremophiles in Space Exploration.Indian J Microbiol. 2024 Jun;64(2):418-428. doi: 10.1007/s12088-024-01297-4. Epub 2024 May 4. Indian J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39010991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aircraft surveys for air eDNA: probing biodiversity in the sky.PeerJ. 2023 Apr 14;11:e15171. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15171. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37077310 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Verseux C, et al. Sustainable life support on Mars—The potential roles of cyanobacteria. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2016;15:65–92. doi: 10.1017/S147355041500021X. - DOI
-
- Cottin H, et al. Space as a tool for astrobiology: Review and recommendations for experimentations in earth orbit and beyond. Space Sci. Rev. 2017;209:83–181. doi: 10.1007/s11214-017-0365-5. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

