ACE2 expression in adipose tissue is associated with cardio-metabolic risk factors and cell type composition-implications for COVID-19
- PMID: 35589964
- PMCID: PMC9119844
- DOI: 10.1038/s41366-022-01136-w
ACE2 expression in adipose tissue is associated with cardio-metabolic risk factors and cell type composition-implications for COVID-19
Abstract
Background: COVID-19 severity varies widely. Although some demographic and cardio-metabolic factors, including age and obesity, are associated with increasing risk of severe illness, the underlying mechanism(s) are uncertain.
Subjects/methods: In a meta-analysis of three independent studies of 1471 participants in total, we investigated phenotypic and genetic factors associated with subcutaneous adipose tissue expression of Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2), measured by RNA-Seq, which acts as a receptor for SARS-CoV-2 cellular entry.
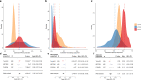
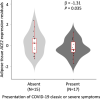
Results: Lower adipose tissue ACE2 expression was associated with multiple adverse cardio-metabolic health indices, including type 2 diabetes (T2D) (P = 9.14 × 10-6), obesity status (P = 4.81 × 10-5), higher serum fasting insulin (P = 5.32 × 10-4), BMI (P = 3.94 × 10-4), and lower serum HDL levels (P = 1.92 × 10-7). ACE2 expression was also associated with estimated proportions of cell types in adipose tissue: lower expression was associated with a lower proportion of microvascular endothelial cells (P = 4.25 × 10-4) and higher proportion of macrophages (P = 2.74 × 10-5). Despite an estimated heritability of 32%, we did not identify any proximal or distal expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) associated with adipose tissue ACE2 expression.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that individuals with cardio-metabolic features known to increase risk of severe COVID-19 have lower background ACE2 levels in this highly relevant tissue. Reduced adipose tissue ACE2 expression may contribute to the pathophysiology of cardio-metabolic diseases, as well as the associated increased risk of severe COVID-19.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Update of
-
ACE2 expression in adipose tissue is associated with COVID-19 cardio-metabolic risk factors and cell type composition.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Aug 14:2020.08.11.20171108. doi: 10.1101/2020.08.11.20171108. medRxiv. 2020. Update in: Int J Obes (Lond). 2022 Aug;46(8):1478-1486. doi: 10.1038/s41366-022-01136-w. PMID: 32817962 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Intensive care national audit & research centre. ICNARC report on COVID-19 in critical care - 04 April 2020. 2020:1–16.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL028481/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M004422/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK093757/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 221574/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- ZIA HG000024/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L01999X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/R023131/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007092/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

