Reversible lysine-targeted probes reveal residence time-based kinase selectivity
- PMID: 35590003
- PMCID: PMC9970282
- DOI: 10.1038/s41589-022-01019-1
Reversible lysine-targeted probes reveal residence time-based kinase selectivity
Abstract
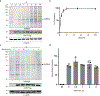
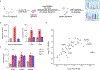
The expansion of the target landscape of covalent inhibitors requires the engagement of nucleophiles beyond cysteine. Although the conserved catalytic lysine in protein kinases is an attractive candidate for a covalent approach, selectivity remains an obvious challenge. Moreover, few covalent inhibitors have been shown to engage the kinase catalytic lysine in animals. We hypothesized that reversible, lysine-targeted inhibitors could provide sustained kinase engagement in vivo, with selectivity driven in part by differences in residence time. By strategically linking benzaldehydes to a promiscuous kinase binding scaffold, we developed chemoproteomic probes that reversibly and covalently engage >200 protein kinases in cells and mice. Probe-kinase residence time was dramatically enhanced by a hydroxyl group ortho to the aldehyde. Remarkably, only a few kinases, including Aurora A, showed sustained, quasi-irreversible occupancy in vivo, the structural basis for which was revealed by X-ray crystallography. We anticipate broad application of salicylaldehyde-based probes to proteins that lack a druggable cysteine.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
T.Y., B.H., P.K., J.R.M., J.C.K., J.D.L., S.N., and J.D.C. are current or former employees of Pfizer. J.T. is a founder of Global Blood Therapeutics, Principia Biopharma, Kezar Life Sciences, Cedilla Therapeutics, and Terremoto Biosciences, and a scientific advisor to Entos.
Figures

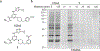

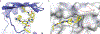

References
-
- Honigberg LA; Smith AM; Sirisawad M; Verner E; Loury D; Chang B; Li S; Pan Z; Thamm DH; Miller RA; Buggy JJ The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 blocks B-cell activation and is efficacious in models of autoimmune disease and B-cell malignancy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107 (29), 13075–13080. https://www.pnas.org/content/pnas/107/29/13075.full.pdf - PMC - PubMed
-
- Byrd JC; Furman RR; Coutre SE; Flinn IW; Burger JA; Blum KA; Grant B; Sharman JP; Coleman M; Wierda WG; Jones JA; Zhao W; Heerema NA; Johnson AJ; Sukbuntherng J; Chang BY; Clow F; Hedrick E; Buggy JJ; James DF; O’Brien S. Targeting BTK with Ibrutinib in Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N Engl J Med 2013, 369 (1), 32–42. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1215637 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Finlay MRV; Anderton M; Ashton S; Ballard P; Bethel PA; Box MR; Bradbury RH; Brown SJ; Butterworth S; Campbell A; Chorley C; Colclough N; Cross DAE; Currie GS; Grist M; Hassall L; Hill GB; James D; James M; Kemmitt P; Klinowska T; Lamont G; Lamont SG; Martin N; McFarland HL; Mellor MJ; Orme JP; Perkins D; Perkins P; Richmond G; Smith P; Ward RA; Waring MJ; Whittaker D; Wells S; Wrigley GL Discovery of a Potent and Selective EGFR Inhibitor (AZD9291) of Both Sensitizing and T790M Resistance Mutations That Spares the Wild Type Form of the Receptor. J Med Chem 2014, 57 (20), 8249–8267. 10.1021/jm500973a - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jänne PA; Yang JC-H; Kim D-W; Planchard D; Ohe Y; Ramalingam SS; Ahn M-J; Kim S-W; Su W-C; Horn L; Haggstrom D; Felip E; Kim J-H; Frewer P; Cantarini M; Brown KH; Dickinson PA; Ghiorghiu S; Ranson M. AZD9291 in EGFR Inhibitor–Resistant Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med 2015, 372 (18), 1689–1699. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1411817 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lanman BA; Allen JR; Allen JG; Amegadzie AK; Ashton KS; Booker SK; Chen JJ; Chen N; Frohn MJ; Goodman G; Kopecky DJ; Liu L; Lopez P; Low JD; Ma V; Minatti AE; Nguyen TT; Nishimura N; Pickrell AJ; Reed AB; Shin Y; Siegmund AC; Tamayo NA; Tegley CM; Walton MC; Wang H-L; Wurz RP; Xue M; Yang KC; Achanta P; Bartberger MD; Canon J; Hollis LS; McCarter JD; Mohr C; Rex K; Saiki AY; San Miguel T; Volak LP; Wang KH; Whittington DA; Zech SG; Lipford JR; Cee VJ Discovery of a Covalent Inhibitor of KRASG12C (AMG 510) for the Treatment of Solid Tumors. J Med Chem 2020, 63 (1), 52–65. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01180 - DOI - PubMed

