Baseline Demographics and Severity and Burden of Atopic Dermatitis in Adult Patients Initiating Dupilumab Treatment in a Real-World Registry (PROSE)
- PMID: 35590038
- PMCID: PMC9209562
- DOI: 10.1007/s13555-022-00742-w
Baseline Demographics and Severity and Burden of Atopic Dermatitis in Adult Patients Initiating Dupilumab Treatment in a Real-World Registry (PROSE)
Abstract
Introduction: Dupilumab was initially approved in 2017 as the first biologic therapy for atopic dermatitis (AD). We characterized adults with AD initiating dupilumab in a real-world setting in the USA/Canada.
Methods: PROSE is an ongoing, longitudinal, prospective, observational, multicenter registry of patients with AD initiating dupilumab per country-specific prescribing information. We report baseline data (day of first dupilumab injection) for patients enrolled from April 2018 through July 2019.
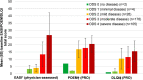
Results: Among 315 patients (mean age 42.5 years, 55.2% female), the median AD duration was 17.0 years; 65.4% reported a history of type 2 inflammatory comorbidities (e.g., allergic rhinitis, asthma), and 93.3% reported treatment(s) for AD in the previous year, including topical corticosteroids (90.8%), systemic corticosteroids (36.2%), and nonsteroidal systemic therapies (14.0%). In total, 89.2% had an Overall Disease Severity score of 3 (moderate) or 4 (severe). Other mean disease severity scores included the following: Eczema Area and Severity Index 16.9 (range 0-72), body surface area affected 26.8%, Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure 18.5 (range 0-28), Dermatology Life Quality Index 12.7 (range 0-30), and pruritus Numerical Rating Scale score 6.9 (range 0-10).
Conclusion: Patients initiating dupilumab have longstanding moderate-to-severe AD with significant disease burden and frequent type 2 comorbidities.
Gov identifier: NCT03428646.
Keywords: Atopic dermatitis; Baseline; Dupilumab; Eczema; Registry.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Real-World Effectiveness of Dupilumab in Adult and Adolescent Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: 2-Year Interim Data from the PROSE Registry.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024 Jan;14(1):261-270. doi: 10.1007/s13555-023-01061-4. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 38175364 Free PMC article.
-
Baseline Demographics, Comorbidities, Treatment Patterns and Burden of Atopic Dermatitis in Adults and Adolescents from the GLOBOSTAD Long-Term Observational Study.Adv Ther. 2023 Dec;40(12):5366-5382. doi: 10.1007/s12325-023-02644-5. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Adv Ther. 2023. PMID: 37801232 Free PMC article.
-
Dupilumab in Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis and Prior Use of Systemic Non-Steroidal Immunosuppressants: Analysis of Four Phase 3 Trials.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021 Aug;11(4):1357-1372. doi: 10.1007/s13555-021-00558-0. Epub 2021 Jun 18. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021. PMID: 34142350 Free PMC article.
-
Dupilumab: A review of its use in the treatment of atopic dermatitis.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Mar;78(3 Suppl 1):S28-S36. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.12.022. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29471919 Review.
-
A Literature Review of Real-World Effectiveness and Safety of Dupilumab for Atopic Dermatitis.JID Innov. 2021 Jul 30;1(3):100042. doi: 10.1016/j.xjidi.2021.100042. eCollection 2021 Sep. JID Innov. 2021. PMID: 34909737 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Real-World Effectiveness of Dupilumab in Adult and Adolescent Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: 2-Year Interim Data from the PROSE Registry.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024 Jan;14(1):261-270. doi: 10.1007/s13555-023-01061-4. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 38175364 Free PMC article.
-
Complete/Near-Complete Itch Response Observed in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis Initiating Dupilumab: 3-Year, Real-World, Interim Data from the PROSE Registry.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2025 Jun;15(6):1523-1531. doi: 10.1007/s13555-025-01395-1. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2025. PMID: 40234297 Free PMC article.
-
The Treat-to-Target Project in Atopic Dermatitis: One Year On.Acta Derm Venereol. 2023 Apr 21;103:adv5382. doi: 10.2340/actadv.v103.5382. Acta Derm Venereol. 2023. PMID: 37083095 Free PMC article.
-
Case report: Successful treatment of non-bullous lichen planus pemphigoides with dupilumab.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 16;9:1023458. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1023458. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36590953 Free PMC article.
-
Baseline Demographics, Comorbidities, Treatment Patterns and Burden of Atopic Dermatitis in Adults and Adolescents from the GLOBOSTAD Long-Term Observational Study.Adv Ther. 2023 Dec;40(12):5366-5382. doi: 10.1007/s12325-023-02644-5. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Adv Ther. 2023. PMID: 37801232 Free PMC article.
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

