Initial TK-deficient HSV-1 infection in the lip alters contralateral lip challenge immune dynamics
- PMID: 35590057
- PMCID: PMC9119387
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-12597-4
Initial TK-deficient HSV-1 infection in the lip alters contralateral lip challenge immune dynamics
Abstract
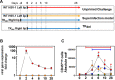
Primary infection with herpes simplex type 1 (HSV-1) occurring around the mouth and nose switches rapidly to lifelong latent infection in sensitive trigeminal ganglia (TG) neurons. Sporadic reactivation of these latent reservoirs later in life is the cause of acute infections of the corneal epithelium, which can cause potentially blinding herpes simplex keratitis (HSK). There is no effective vaccine to protect against HSK, and antiviral drugs provide only partial protection against recurrences. We previously engendered an acute disease-free, non-reactivating latent state in mice when challenged with virulent HSV-1 in orofacial mucosa, by priming with non-neurovirulent HSV-1 (TKdel) before the challenge. Herein, we define the local immune infiltration and inflammatory chemokine production changes after virulent HSV-1 challenge, which were elicited by TKdel prime. Heightened immunosurveillance before virulent challenge, and early enhanced lymphocyte-enriched infiltration of the challenged lip were induced, which corresponded to attenuation of inflammation in the TG and enhanced viral control. Furthermore, classical latent-phase T cell persistence around latent HSV-1 reservoirs were severely reduced. These findings identify the immune processes that are likely to be responsible for establishing non-reactivating latent HSV-1 reservoirs. Stopping reactivation is essential for development of efficient vaccine strategies against HSV-1.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Replication, Ocular Disease, and Reactivations from Latency Are Restricted Unilaterally after Inoculation of Virus into the Lip.J Virol. 2019 Nov 26;93(24):e01586-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01586-19. Print 2019 Dec 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31554680 Free PMC article.
-
Human Asymptomatic Epitope Peptide/CXCL10-Based Prime/Pull Vaccine Induces Herpes Simplex Virus-Specific Gamma Interferon-Positive CD107+ CD8+ T Cells That Infiltrate the Corneas and Trigeminal Ganglia of Humanized HLA Transgenic Rabbits and Protect against Ocular Herpes Challenge.J Virol. 2018 Jul 31;92(16):e00535-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00535-18. Print 2018 Aug 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29899087 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuated Herpes Simplex Virus 1 (HSV-1) Expressing a Mutant Form of ICP6 Stimulates a Strong Immune Response That Protects Mice against HSV-1-Induced Corneal Disease.J Virol. 2018 Aug 16;92(17):e01036-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01036-18. Print 2018 Sep 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29950407 Free PMC article.
-
[Battle with herpes for 37 years].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2015 Mar;119(3):145-66; discussion 167. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2015. PMID: 25854108 Review. Japanese.
-
[Herpes simplex virus latency, reactivation, and a new antiviral therapy for herpetic keratitis].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2008 Mar;112(3):247-64; discussion 265. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2008. PMID: 18411713 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Viral infection and antiviral immunity in the oral cavity.Nat Rev Immunol. 2025 Apr;25(4):235-249. doi: 10.1038/s41577-024-01100-x. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Nat Rev Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39533045 Review.
-
Herpes simplex keratitis: A brief clinical overview.World J Virol. 2024 Mar 25;13(1):89934. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v13.i1.89934. World J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38616855 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

