The DNA/RNA helicase DHX9 contributes to the transcriptional program of the androgen receptor in prostate cancer
- PMID: 35590370
- PMCID: PMC9118622
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-022-02384-4
The DNA/RNA helicase DHX9 contributes to the transcriptional program of the androgen receptor in prostate cancer
Abstract
Background: Prostate cancer (PC) is the most commonly diagnosed male malignancy and an important cause of mortality. Androgen deprivation therapy is the first line treatment but, unfortunately, a large part of patients evolves to a castration-resistant stage, for which no effective cure is currently available. The DNA/RNA helicase DHX9 is emerging as an important regulator of cellular processes that are often deregulated in cancer.
Methods: To investigate whether DHX9 modulates PC cell transcriptome we performed RNA-sequencing analyses upon DHX9 silencing in the androgen-responsive cell line LNCaP. Bioinformatics and functional analyses were carried out to elucidate the mechanism of gene expression regulation by DHX9. Data from The Cancer Genome Atlas were mined to evaluate the potential role of DHX9 in PC.
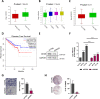
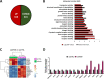
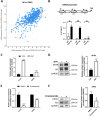
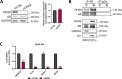
Results: We found that up-regulation of DHX9 correlates with advanced stage and is associated with poor prognosis of PC patients. High-throughput RNA-sequencing analysis revealed that depletion of DHX9 in androgen-sensitive LNCaP cells affects expression of hundreds of genes, which significantly overlap with known targets of the Androgen Receptor (AR). Notably, AR binds to the DHX9 promoter and induces its expression, while Enzalutamide-mediated inhibition of AR activity represses DHX9 expression. Moreover, DHX9 interacts with AR in LNCaP cells and its depletion significantly reduced the recruitment of AR to the promoter region of target genes and the ability of AR to promote their expression in response to 5α-dihydrotestosterone. Consistently, silencing of DXH9 negatively affected androgen-induced PC cell proliferation and migration.
Conclusions: Collectively, our data uncover a new role of DHX9 in the control of the AR transcriptional program and establish the existence of an oncogenic DHX9/AR axis, which may represent a new druggable target to counteract PC progression.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

