Angular-Resolved Thomson Parabola Spectrometer for Laser-Driven Ion Accelerators
- PMID: 35590929
- PMCID: PMC9104512
- DOI: 10.3390/s22093239
Angular-Resolved Thomson Parabola Spectrometer for Laser-Driven Ion Accelerators
Abstract
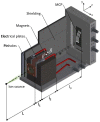
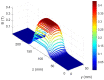
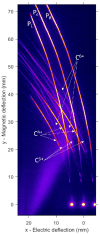
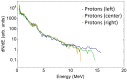
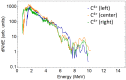
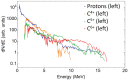
This article reports the development, construction, and experimental test of an angle-resolved Thomson parabola (TP) spectrometer for laser-accelerated multi-MeV ion beams in order to distinguish between ionic species with different charge-to-mass ratio. High repetition rate (HHR) compatibility is guaranteed by the use of a microchannel plate (MCP) as active particle detector. The angular resolving power, which is achieved due to an array of entrance pinholes, can be simply adjusted by modifying the geometry of the experiment and/or the pinhole array itself. The analysis procedure allows for different ion traces to cross on the detector plane, which greatly enhances the flexibility and capabilities of the detector. A full characterization of the TP magnetic field is implemented into a relativistic code developed for the trajectory calculation of each pinhole beamlet. We describe the first test of the spectrometer at the 1PW VEGA 3 laser facility at CLPU, Salamanca (Spain), where up to 15MeV protons and carbon ions from a 3μm laser-irradiated Al foil are detected.
Keywords: charged-particle spectroscopy; instrumentation; ion beams; plama diagnostics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Strickland D., Mourou G. Compression of amplified chirped optical pulses. Opt. Commun. 1985;55:447–449. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(85)90151-8. - DOI
-
- Yoon J.W., Kim Y.G., Choi I.W., Sung J.H., Lee H.W., Lee S.K., Nam C.H. Realization of laser intensity over 1023W/cm2. Optica. 2021;8:630–635. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.420520. - DOI
-
- Macchi A., Borghesi M., Passoni M. Ion acceleration by superintense laser-plasma interaction. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2013;85:751–793. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.85.751. - DOI
-
- Esarey E., Schroeder C.B., Leemans W.P. Physics of laser-driven plasma-based electron accelerators. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009;81:1229–1285. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.81.1229. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

