A Deep Learning Approach for the Assessment of Signal Quality of Non-Invasive Foetal Electrocardiography
- PMID: 35591004
- PMCID: PMC9103336
- DOI: 10.3390/s22093303
A Deep Learning Approach for the Assessment of Signal Quality of Non-Invasive Foetal Electrocardiography
Abstract
Non-invasive foetal electrocardiography (NI-FECG) has become an important prenatal monitoring method in the hospital. However, due to its susceptibility to non-stationary noise sources and lack of robust extraction methods, the capture of high-quality NI-FECG remains a challenge. Recording waveforms of sufficient quality for clinical use typically requires human visual inspection of each recording. A Signal Quality Index (SQI) can help to automate this task but, contrary to adult ECG, work on SQIs for NI-FECG is sparse. In this paper, a multi-channel signal quality classifier for NI-FECG waveforms is presented. The model can be used during the capture of NI-FECG to assist technicians to record high-quality waveforms, which is currently a labour-intensive task. A Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is trained to distinguish between NI-FECG segments of high and low quality. NI-FECG recordings with one maternal channel and three abdominal channels were collected from 100 subjects during a routine hospital screening (102.6 min of data). The model achieves an average 10-fold cross-validated AUC of 0.95 ± 0.02. The results show that the model can reliably assess the FECG signal quality on our dataset. The proposed model can improve the automated capture and analysis of NI-FECG as well as reduce technician labour time.
Keywords: convolutional neural network; foetal ECG; signal quality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


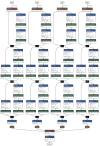


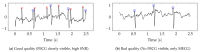


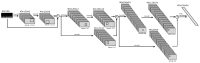

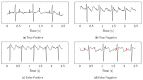

Similar articles
-
A deep learning approach for fetal QRS complex detection.Physiol Meas. 2018 Apr 20;39(4):045004. doi: 10.1088/1361-6579/aab297. Physiol Meas. 2018. PMID: 29485406
-
A practical guide to non-invasive foetal electrocardiogram extraction and analysis.Physiol Meas. 2016 May;37(5):R1-R35. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/37/5/R1. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Physiol Meas. 2016. PMID: 27067431 Review.
-
Non-invasive Fetal ECG Signal Quality Assessment for Multichannel Heart Rate Estimation.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2017 Dec;64(12):2793-2802. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2017.2675543. Epub 2017 Mar 1. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2017. PMID: 28362581
-
Non-invasive Fetal ECG Signal Quality Assessment based on Unsupervised Learning Approach.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2022 Jul;2022:1296-1299. doi: 10.1109/EMBC48229.2022.9870908. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2022. PMID: 36086629
-
Noninvasive fetal electrocardiography: an overview of the signal electrophysiological meaning, recording procedures, and processing techniques.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2015 Jul;20(4):303-13. doi: 10.1111/anec.12259. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2015. PMID: 25640061 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Fetal electrocardiogram signal extraction and analysis method combining fast independent component analysis algorithm and convolutional neural network].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2023 Feb 25;40(1):51-59. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202210071. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 36854548 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Review of Non-Invasive Fetal Electrocardiography Monitoring Techniques.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Feb 26;25(5):1412. doi: 10.3390/s25051412. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40096208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Automatic signal quality assessment of raw trans-abdominal biopotential recordings for non-invasive fetal electrocardiography.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Feb 27;11:1059119. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1059119. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36923461 Free PMC article.
-
Fetal Arrhythmia Detection Based on Labeling Considering Heartbeat Interval.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Dec 30;10(1):48. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10010048. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36671621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martinek R., Kahankova R., Jezewski J., Jaros R., Mohylova J., Fajkus M., Nedoma J., Janku P., Nazeran H. Comparative effectiveness of ICA and PCA in extraction of fetal ECG from abdominal signals: Toward non-invasive fetal monitoring. Front. Physiol. 2018;9:648. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00648. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jagannath D., Selvakumar A.I. Issues and research on foetal electrocardiogram signal elicitation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2014;10:224–244. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2013.11.001. - DOI
-
- Adithya P.C., Sankar R., Moreno W.A., Hart S. Trends in fetal monitoring through phonocardiography: Challenges and future directions. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2017;33:289–305. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2016.11.007. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

