Multiscale and Hierarchical Feature-Aggregation Network for Segmenting Medical Images
- PMID: 35591129
- PMCID: PMC9104396
- DOI: 10.3390/s22093440
Multiscale and Hierarchical Feature-Aggregation Network for Segmenting Medical Images
Abstract
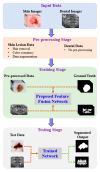
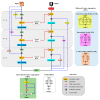
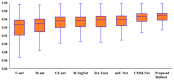
We propose an encoder-decoder architecture using wide and deep convolutional layers combined with different aggregation modules for the segmentation of medical images. Initially, we obtain a rich representation of features that span from low to high levels and from small to large scales by stacking multiple k × k kernels, where each k × k kernel operation is split into k × 1 and 1 × k convolutions. In addition, we introduce two feature-aggregation modules-multiscale feature aggregation (MFA) and hierarchical feature aggregation (HFA)-to better fuse information across end-to-end network layers. The MFA module progressively aggregates features and enriches feature representation, whereas the HFA module merges the features iteratively and hierarchically to learn richer combinations of the feature hierarchy. Furthermore, because residual connections are advantageous for assembling very deep networks, we employ an MFA-based long residual connections to avoid vanishing gradients along the aggregation paths. In addition, a guided block with multilevel convolution provides effective attention to the features that were copied from the encoder to the decoder to recover spatial information. Thus, the proposed method using feature-aggregation modules combined with a guided skip connection improves the segmentation accuracy, achieving a high similarity index for ground-truth segmentation maps. Experimental results indicate that the proposed model achieves a superior segmentation performance to that obtained by conventional methods for skin-lesion segmentation, with an average accuracy score of 0.97 on the ISIC-2018, PH2, and UFBA-UESC datasets.
Keywords: convolutional neural network; feature fusion; medical-image segmentation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MFA-Net: Multiple Feature Association Network for medical image segmentation.Comput Biol Med. 2023 May;158:106834. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106834. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Comput Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37003067
-
Ms RED: A novel multi-scale residual encoding and decoding network for skin lesion segmentation.Med Image Anal. 2022 Jan;75:102293. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2021.102293. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Med Image Anal. 2022. PMID: 34800787
-
Automatic segmentation of spine x-ray images based on multiscale feature enhancement network.Med Phys. 2024 Oct;51(10):7282-7294. doi: 10.1002/mp.17278. Epub 2024 Jun 30. Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38944886
-
EIU-Net: Enhanced feature extraction and improved skip connections in U-Net for skin lesion segmentation.Comput Biol Med. 2023 Aug;162:107081. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107081. Epub 2023 May 29. Comput Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37301097 Review.
-
A Review on Multiscale-Deep-Learning Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Sep 28;22(19):7384. doi: 10.3390/s22197384. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36236483 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Review of Recent Advances in Artificial Intelligence for Dentistry E-Health.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jun 28;13(13):2196. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13132196. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37443594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Image Segmentation Method Based on Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and Sequence Relationship Learning.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 7;23(2):690. doi: 10.3390/s23020690. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679487 Free PMC article.
-
Semi-supervised auto-segmentation method for pelvic organ-at-risk in magnetic resonance images based on deep-learning.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Feb 22;25(3):e14296. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14296. Online ahead of print. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38386963 Free PMC article.
-
Performance and Robustness of Regional Image Segmentation Driven by Selected Evolutionary and Genetic Algorithms: Study on MR Articular Cartilage Images.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Aug 23;22(17):6335. doi: 10.3390/s22176335. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36080793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang G., Li W., Zuluaga M.A., Pratt R., Patel P.A., Aertsen M., Doel T., David A.L., Deprest J., Ourselin S., et al. Interactive medical image segmentation using deep learning with image-specific fine tuning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 2018;37:1562–1573. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2791721. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

