Advantages of Cubosomal Formulation for Gatifloxacin Delivery in the Treatment of Bacterial Keratitis: In Vitro and In Vivo Approach Using Clinical Isolate of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 35591708
- PMCID: PMC9104145
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15093374
Advantages of Cubosomal Formulation for Gatifloxacin Delivery in the Treatment of Bacterial Keratitis: In Vitro and In Vivo Approach Using Clinical Isolate of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
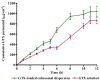
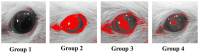
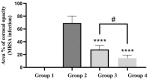
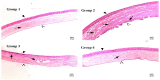
The objective of this study was to enhance the corneal permeation of gatifloxacin (GTX) using cubosomal nanoparticle as a delivery system. Cubosomal nanoparticle loaded with GTX was prepared and subjected for in vitro and in vivo investigations. The prepared GTX-loaded cubosomal particles exhibited nanoparticle size of 197.46 ± 9.40 nm and entrapment efficiency of 52.8% ± 2.93. The results of ex vivo corneal permeation of GTX-loaded cubosomal dispersion show approximately 1.3-fold increase compared to GTX aqueous dispersion. The incorporation of GTX into cubosomal particles resulted in a fourfold reduction in the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) value for the GTX cubosomal particles relative to GTX aqueous dispersion. Furthermore, the enhanced corneal penetration of GTX-loaded cubosomal dispersion compared was evident by a significant decrease in the area % of corneal opacity in MRSA infected rats. Moreover, these results were confirmed by photomicrographs of histological structures of corneal tissues from rats treated with GTX-cubosomal dispersion which did not present any change compared to that of the normal rat corneas. In conclusion, treatment of ocular bacterial infections and reduction in the probability of development of new resistant strains of MRSA could be accomplished with GTX-loaded cubosomal nanoparticles.
Keywords: MIC; corneal permeation; cubosomal dispersion; gatifloxacin; keratitis; methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Celecoxib-Loaded Cubosomal Nanoparticles as a Therapeutic Approach for Staphylococcus aureus In Vivo Infection.Microorganisms. 2023 Sep 6;11(9):2247. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11092247. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37764091 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of cubosomal nanoparticles as an ocular delivery system for fluconazole in treatment of keratomycosis.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2020 Dec;10(6):1841-1852. doi: 10.1007/s13346-020-00830-4. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 32779112
-
Gatifloxacin Loaded Nano Lipid Carriers for the Management of Bacterial Conjunctivitis.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Aug 15;12(8):1318. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12081318. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627738 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic Resistance in the Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus Keratitis: a 20-Year Review.Cornea. 2015 Jun;34(6):698-703. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000000431. Cornea. 2015. PMID: 25811722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new target for Staphylococcus aureus associated with keratitis.Cornea. 2011 Oct;30 Suppl 1:S34-40. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0b013e3182282100. Cornea. 2011. PMID: 21912228 Review.
Cited by
-
Celecoxib-Loaded Cubosomal Nanoparticles as a Therapeutic Approach for Staphylococcus aureus In Vivo Infection.Microorganisms. 2023 Sep 6;11(9):2247. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11092247. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37764091 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Bacterial Keratitis Treatment with Polyethylene Glycol-Dithiothreitol-Boric Acid Hydrogel and Gatifloxacin.Curr Drug Deliv. 2024;21(11):1548-1558. doi: 10.2174/0115672018279105240226050253. Curr Drug Deliv. 2024. PMID: 38425110
-
Formulation and physicochemical characterization of azithromycin-loaded cubosomes.Res Pharm Sci. 2022 Dec 24;18(1):49-58. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.363595. eCollection 2023 Feb. Res Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 36846738 Free PMC article.
-
Insights on Development Aspects of Polymeric Nanocarriers: The Translation from Bench to Clinic.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Aug 29;14(17):3545. doi: 10.3390/polym14173545. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36080620 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nguyen D.D., Lai J.-Y. Synthesis, bioactive properties, and biomedical applications of intrinsically therapeutic nanoparticles for disease treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2022;435:134970. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.134970. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

