Pneumoparotid related to obstructive sleep apnea syndrome treated by oral appliance with anterior opening to reduce intraoral pressure
- PMID: 35592044
- PMCID: PMC9097368
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.5816
Pneumoparotid related to obstructive sleep apnea syndrome treated by oral appliance with anterior opening to reduce intraoral pressure
Abstract
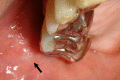
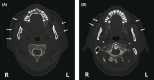
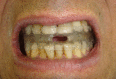
Pneumoparotid is associated with retrograde air insufflation in Stensen's duct and the parotid gland. A 57-year-old man experienced swelling and pain in the right parotid region after sleeping during a flight. Pneumoparotid and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome were diagnosed. Pneumoparotid was suspected as caused by increased intraoral pressure during sleep; thus, an oral appliance to reduce intraoral pressure was effective. After 9 years, the symptoms recurred on the left side. The appliance was reinserted and helped substantially. This is the first case report of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome accompanying pneumoparotid, treated effectively with an oral appliance, with a 10-year follow-up.
Keywords: obstructive sleep apnea syndrome; oral appliance therapy; parotid gland; parotid swelling; pneumoparotid.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Etiology of Pneumoparotid: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2022 Dec 24;12(1):144. doi: 10.3390/jcm12010144. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36614949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pneumoparotid: a rare cause of parotid swelling in a 7-year-old child.B-ENT. 2011;7(4):297-300. B-ENT. 2011. PMID: 22338245
-
Pneumoparotid: A Rare Consequence of Being a Saxophonist.Cureus. 2024 Nov 11;16(11):e73497. doi: 10.7759/cureus.73497. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39669821 Free PMC article.
-
Multislice computed tomography of pneumoparotid: a case report.Radiat Med. 2005 Mar;23(2):147-50. Radiat Med. 2005. PMID: 15827536
-
Pneumoparotid and Pneumoparotitis: A Literary Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jun 2;17(11):3936. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17113936. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32498334 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Etiology of Pneumoparotid: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2022 Dec 24;12(1):144. doi: 10.3390/jcm12010144. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36614949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pneumoparotid with imaging findings: A case report and review of literature.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Dec 6;12(34):6705-6714. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i34.6705. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 39650813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hyrtl J, ed. Vordere Mundhöhle. In: Handbuch der topographischen Anatomie und ihrer praktisch medicinisch‐chirurgischen Anwendungen 5th ed. Braumüller; 1865:390.
-
- Deichmüller . Luftgeschwulst der Wange (Pneumatozele). Berl Klin Wochenschr. 1890;54:1226.
-
- Scheele . Über Glasbläsern und seine Komplikationen. Berl Klin Wochenschr. 1900;10:207‐210, 241‐244.
-
- Scheier M. Über die Krankheiten der Mundhöhle bei Glasbläsern. Arch f Laryngol. 1907;19:472‐496.
-
- Rysenaer L, van Deinse J, Stuyt LB. Pneumo‐parotidite récidivante. Pract Oto Rhinolaryngol. 1963;25:128‐131. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

