A review on the potential of photocatalysis in combatting SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater
- PMID: 35592059
- PMCID: PMC8084616
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102111
A review on the potential of photocatalysis in combatting SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater
Abstract
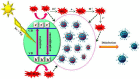
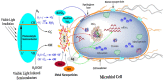
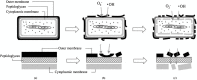
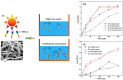
Photocatalytic technology offers powerful virus disinfection in wastewater via oxidative capability with minimum harmful by-products generation. This review paper aims to provide state-of-the-art photocatalytic technology in battling transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in wastewater. Prior to that, the advantages and limitations of the existing conventional and advanced oxidation processes for virus disinfection in water systems were thoroughly examined. A wide spectrum of virus degradation by various photocatalysts was then considered to understand the potential mechanism for deactivating this deadly virus. The challenges and future perspectives were comprehensively discussed at the end of this review describing the limitations of current photocatalytic technology and suggesting a realistic outlook on advanced photocatalytic technology as a potential solution in dealing with similar upcoming pandemics. The major finding of this review including discovery of a vision on the possible photocatalytic approaches that have been proven to be outstanding against other viruses and subsequently combatting SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater. This review intends to deliver insightful information and discussion on the potential of photocatalysis in battling COVID-19 transmission through wastewater.
Keywords: COVID-19; Photocatalysis; SARS-CoV-2; Virus; Wastewater.
© 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- He Y., Sutton N.B., Rijnaarts H.H.H., Langenhoff A.A.M. Degradation of pharmaceuticals in wastewater using immobilized TiO2 photocatalysis under simulated solar irradiation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016;182:132–141. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.09.015. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
