Paradoxical Reasoning: An fMRI Study
- PMID: 35592168
- PMCID: PMC9113220
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.850491
Paradoxical Reasoning: An fMRI Study
Abstract
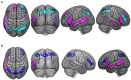
Paradoxes are a special form of reasoning leading to absurd inferences in contrast to logical reasoning that is used to reach valid conclusions. A functional MRI (fMRI) study was conducted to investigate the neural substrates of paradoxical and deductive reasoning. Twenty-four healthy participants were scanned using fMRI, while they engaged in reasoning tasks based on arguments, which were either Zeno's like paradoxes (paradoxical reasoning) or Aristotelian arguments (deductive reasoning). Clusters of significant activation for paradoxical reasoning were located in bilateral inferior frontal and middle temporal gyrus. Clusters of significant activation for deductive reasoning were located in bilateral superior and inferior parietal lobe, precuneus, and inferior frontal gyrus. These results confirmed that different brain activation patterns are engaged for paradoxical vs. deductive reasoning providing a basis for future studies on human physiological as well as pathological reasoning.
Keywords: deductive reasoning; fMRI; fronto-parietal brain activation patterns; fronto-temporal brain activation patterns; paradoxical syllogism.
Copyright © 2022 Belekou, Papageorgiou, Karavasilis, Tsaltas, Kelekis, Klein and Smyrnis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Barnes J. (1995). The Complete Works of Aristotle: The Revised Oxford Translation. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 39–113.
-
- Braine M., O’Brien D. (1998). Mental Logic (1st Edn). New York: Psychology Press
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

