Intranasal Delivery of Thermostable Subunit Vaccine for Cross-Reactive Mucosal and Systemic Antibody Responses Against SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 35592324
- PMCID: PMC9110812
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.858904
Intranasal Delivery of Thermostable Subunit Vaccine for Cross-Reactive Mucosal and Systemic Antibody Responses Against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
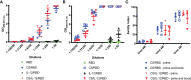
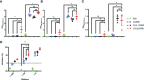
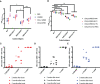
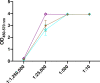
Despite the remarkable efficacy of currently approved COVID-19 vaccines, there are several opportunities for continued vaccine development against SARS-CoV-2 and future lethal respiratory viruses. In particular, restricted vaccine access and hesitancy have limited immunization rates. In addition, current vaccines are unable to prevent breakthrough infections, leading to prolonged virus circulation. To improve access, a subunit vaccine with enhanced thermostability was designed to eliminate the need for an ultra-cold chain. The exclusion of infectious and genetic materials from this vaccine may also help reduce vaccine hesitancy. In an effort to prevent breakthrough infections, intranasal immunization to induce mucosal immunity was explored. A prototype vaccine comprised of receptor-binding domain (RBD) polypeptides formulated with additional immunoadjuvants in a chitosan (CS) solution induced high levels of RBD-specific antibodies in laboratory mice after 1 or 2 immunizations. Antibody responses were durable with high titers persisting for at least five months following subcutaneous vaccination. Serum anti-RBD antibodies contained both IgG1 and IgG2a isotypes suggesting that the vaccine induced a mixed Th1/Th2 response. RBD vaccination without CS formulation resulted in minimal anti-RBD responses. The addition of CpG oligonucleotides to the CS plus RBD vaccine formulation increased antibody titers more effectively than interleukin-12 (IL-12). Importantly, generated antibodies were cross-reactive against RBD mutants associated with SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern, including alpha, beta and delta variants, and inhibited binding of RBD to its cognate receptor angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). With respect to stability, vaccines did not lose activity when stored at either room temperature (21-22°C) or 4°C for at least one month. When delivered intranasally, vaccines induced RBD-specific mucosal IgA antibodies, which may protect against breakthrough infections in the upper respiratory tract. Altogether, data indicate that the designed vaccine platform is versatile, adaptable and capable of overcoming key constraints of current COVID-19 vaccines.
Keywords: COVID-19; CpG; Intranasal vaccination; Receptor binding domain (RBD); SARS-CoV-2; chitosan; mucosal immunity.
Copyright © 2022 Nguyen, Mantooth, Vrabel and Zaharoff.
Conflict of interest statement
DZ is a consultant for Checkmate Pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Intranasal vaccination induced cross-protective secretory IgA antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants with reducing the potential risk of lung eosinophilic immunopathology.Vaccine. 2022 Sep 29;40(41):5892-5903. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2022.08.049. Epub 2022 Aug 26. Vaccine. 2022. PMID: 36064667 Free PMC article.
-
A Glycosylated RBD Protein Induces Enhanced Neutralizing Antibodies against Omicron and Other Variants with Improved Protection against SARS-CoV-2 Infection.J Virol. 2022 Sep 14;96(17):e0011822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00118-22. Epub 2022 Aug 16. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35972290 Free PMC article.
-
Broad immunity to SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern mediated by a SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain protein vaccine.EBioMedicine. 2023 Jun;92:104574. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104574. Epub 2023 May 4. EBioMedicine. 2023. PMID: 37148585 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of spike mutated variants of SARS-CoV2 [Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, and Lambda] on the efficacy of subunit recombinant vaccines.Braz J Infect Dis. 2021 Jul-Aug;25(4):101606. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2021.101606. Epub 2021 Aug 17. Braz J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34428473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upper respiratory tract mucosal immunity for SARS-CoV-2 vaccines.Trends Mol Med. 2023 Apr;29(4):255-267. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2023.01.003. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Trends Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36764906 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chitosan-Based Nanomaterial as Immune Adjuvant and Delivery Carrier for Vaccines.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Nov 11;10(11):1906. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10111906. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36423002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of primary immunization route on the outcome of infection with SARS-CoV-2 in a hamster model of COVID-19.Front Microbiol. 2023 May 24;14:1212179. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1212179. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37293233 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Polymeric Composites Derived from Animals, Plants, and Microbes for Vaccine Delivery and Adjuvant Applications: A Review.Gels. 2023 Mar 15;9(3):227. doi: 10.3390/gels9030227. Gels. 2023. PMID: 36975676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Dual-Adjuvanted Parenteral-Intranasal Subunit Nanovaccine generates Robust Systemic and Mucosal Immunity Against SARS-CoV-2 in Mice.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Dec;11(45):e2402792. doi: 10.1002/advs.202402792. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39352717 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody Avidity Maturation Following Booster Vaccination with an Intranasal Adenovirus Salnavac Vaccine.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Dec 2;12(12):1362. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12121362. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39772024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schneider EC, Shah A, Sah P, Moghadas SM, Vilches T, Galvani A. The U.S. COVID-19 Vaccination Program at One Year: How Many Deaths and Hospitalizations Were Averted? New York: : Commonwealth Fund; (2021).
-
- Walensky DR. The AP Interview: CDC Chief Says Omicron Mostly Mild So Far. Stobbe M, editor. New York: Associated Press, (2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

