Neutrophil Count Predicts Malignant Cerebellar Edema and Poor Outcome in Acute Basilar Artery Occlusion Receiving Endovascular Treatment: A Nationwide Registry-Based Study
- PMID: 35592334
- PMCID: PMC9111017
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.835915
Neutrophil Count Predicts Malignant Cerebellar Edema and Poor Outcome in Acute Basilar Artery Occlusion Receiving Endovascular Treatment: A Nationwide Registry-Based Study
Abstract
Background: Acute basilar artery occlusion (ABAO) is known to have a poor outcome with a high rate of morbidity and mortality despite endovascular treatment (EVT), highlighting the necessities of exploring factors to limit the efficacy of EVT in these patients. Cerebellar infarctions in ABAO might progress to malignant cerebellar edema (MCE), a life-threatening complication after reperfusion, posing a secondary injury to the brainstem by mass effects. Therefore, the present research aimed to explore the impacts of MCE on a long-term outcome and investigate the prognostic factors for MCE among ABAO after EVT.
Methods: In the national BASILAR registry, a total of 329 ABO patients with cerebellar infarctions treated by EVT met the inclusion criteria. The presence of MCE defined by the Jauss scale ≥4 points, was evaluated on the computed tomography performed 72 h after EVT. The adjusted odds ratio and 95% CI were obtained by logistic regression models. A favorable outcome was defined as a 90-day modified Rankin Scale score of 0-3.
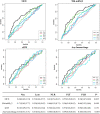
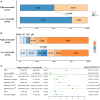
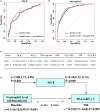
Results: MCE was statistically associated with the decreased incidence of a favorable outcome [adjusted odds ratio, 0.35(95% CI, 0.18-0.68), P=0.002]. The baseline National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score, collateral circulation, neutrophil count at admission, and recanalization status were predictors for MCE and a favorable functional status at 90 days (all P<0.05). Among all inflammatory factors, the neutrophil count achieved the highest accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity for MCE. Adding the neutrophil count status into the baseline model obviously enhanced its prediction ability for MCE and favorable outcome by increasing the area under curve and achieving both net reclassification and integrated discrimination improvement (all P<0.05). Mediation analysis indicated that MCE mediated the association between the increased neutrophil count and worse functional outcome (P=0.026).
Discussion: MCE acted essential roles in worsening prognosis for ABAO after EVT. A high neutrophil count at admission was linked to MCE and a poor outcome among ABAO patients, which could be further incorporated into the clinical decision-making system and guide immunomodulation therapy.
Keywords: acute basilar artery occlusion; endovascular treatment; malignant cerebellar edema; neutrophil count; outcome.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Li, Liu, Chen, Sang, Yang, Zhou and Zi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Outcomes of Endovascular Therapy in Acute Basilar Artery Occlusion With Severe Symptoms.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Dec 1;4(12):e2139550. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.39550. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34913974 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence, predictors, and outcomes of malignant cerebral edema in acute basilar artery occlusion after endovascular treatment: a secondary analysis of the ATTENTION trial.J Neurosurg. 2024 Apr 5;141(4):1011-1019. doi: 10.3171/2024.1.JNS232085. Print 2024 Oct 1. J Neurosurg. 2024. PMID: 38579342 Clinical Trial.
-
Low neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios predict favorable outcomes after endovascular treatment in acute basilar artery occlusion: subgroup analysis of the BASILAR registry.BMC Neurol. 2023 Mar 20;23(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s12883-023-03161-2. BMC Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36941577 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Nomogram for Predicting Malignant Cerebral Edema After Endovascular Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Retrospective Cohort Study.World Neurosurg. 2023 May;173:e548-e558. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2023.02.091. Epub 2023 Feb 25. World Neurosurg. 2023. PMID: 36842531
-
Futile Recanalization After Endovascular Treatment in Patients With Acute Basilar Artery Occlusion.Neurosurgery. 2023 May 1;92(5):1006-1012. doi: 10.1227/neu.0000000000002313. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Neurosurgery. 2023. PMID: 36700757
Cited by
-
Asymmetric deep cerebral venous filling predicts poor outcome of acute basilar artery occlusion after endovascular treatment.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Apr;30(4):e14513. doi: 10.1111/cns.14513. Epub 2023 Nov 12. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 37953498 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of massive cerebellar infarction on the outcomes of patients with acute basilar artery occlusion during hospitalization after endovascular treatment: A retrospective study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Jul 21;102(29):e34154. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034154. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37478217 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

