Troponins in myocardial infarction and injury
- PMID: 35592367
- PMCID: PMC9081942
- DOI: 10.18773/austprescr.2022.006
Troponins in myocardial infarction and injury
Abstract
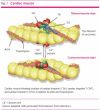
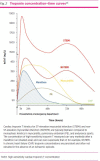
Troponins are proteins that are integral components of the contractile mechanism of muscle, including cardiac muscle. Cardiac troponins Iand T can be detected in the blood of most people after puberty, at concentrations reflecting cardiac mass, sex and age. Current laboratory assays are approximately 1000 times more sensitive than those used previously. They also have higher sensitivity than point-of-care assays. The measurement of cardiac troponins is used primarily to assist in the diagnosis or exclusion of myocardial injury. Serial tests in acute coronary syndrome are guided by the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction.
Keywords: acute coronary syndromes; cardiac troponins; myocardial infarction; point-of-care testing.
(c) NPS MedicineWise.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: none declared
Figures
References
-
- Hopper I. Cardiac effects of non-cardiac drugs. Aust Prescr 2011;34:52-4. 10.18773/austprescr.2011.030 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources