Reliability, Satisfaction and Effectiveness of Benralizumab Home Self-Administration in Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma in Real-World Practice: The Auto-Benra Study
- PMID: 35592384
- PMCID: PMC9113658
- DOI: 10.2147/JAA.S358738
Reliability, Satisfaction and Effectiveness of Benralizumab Home Self-Administration in Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma in Real-World Practice: The Auto-Benra Study
Abstract
Introduction: The increase in drugs available for severe uncontrolled asthma and the lifestyle of these patients make it necessary to implement self-administration programs of these therapies at home. Benralizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting IL5R, was authorized in Spain for poorly controlled severe eosinophilic asthma. The possibility of administration at home was approved in March 2020 in Spain. The aim of the Auto-Benra study was to evaluate the usability and satisfaction of the benralizumab prefilled syringe and autoinjector and assessing the effectivity of these devices in uncontrolled severe eosinophilic asthma (SEA) in home-self administration.
Methods: This is a retrospective, observational multicenter study uncontrolled SEA patients treated with benralizumab at least with 3 doses self-administered at home before April 30, 2021. Reliability and satisfaction with benralizumab at home were evaluated with subcutaneous administration assessment questionnaire (SQAAQ) and visual analogic scales (VAS). Effectiveness was evaluated in all patients with asthma control test (ACT), Mini Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire (MiniAQLQ), annual exacerbation rate, oral corticosteroid treatment (OCS) and asthma-related hospitalizations and emergency visits.
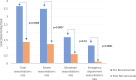
Results: Fifty-four patients across 9 hospitals in Spain were included. The mean SQAAQ score was 6.89 (±0.16) points. Patients and their caregivers and doctors report excellent satisfaction by VAS, with no differences between benralizumab devices used (prefilled syringe and autoinjector). Severe exacerbation rate decreased by 65% (p = 0.0007) after benralizumab treatment. ACT score improved on average 6.27 ± 5.35 points (p < 0.0001) and the mean MiniAQLQ increased up to 1.58 ± 1.47 points (p < 0.0001). Twenty-four patients were OCS-dependent and at the end of study 14 patients get complete OCS withdrawal.
Conclusion: AUTO-BENRA study supports the use of benralizumab at home given the excellent results of satisfaction and usability by patients and their caregivers.
Keywords: benralizumab; eosinophilic asthma; self-administration; severe asthma; severe eosinophilic asthma.
© 2022 García-Moguel et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Ismael Garcia-Moguel reports grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca, GSK, TEVA, SANOFI, NOVARTIS, CHIESI, ORION PHARMA, LETI, ALLERGY THERAPEUTICS, and STALLERGENES during the conduct of the study and has been on advisory boards and/or been a speaker or investigator for: Novartis, AstraZeneca, Teva, GSK, Sanofi Genzyme, Chiesi, Allergy therapeutics, Leti, Stallergenes, ALK-Abelló, Mundipharma, Pfizer and Orion Pharma. Ana Rosado reports personal fees from GSK, Astra-Zeneca, and Novartis, outside the submitted work, has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing and/or educational events from AstraZeneca, GSK, Novartis, and support for attending meetings and/or travel from GSK and Chiesi. Aida Gomez Cardeñosa reports personal fees from ASTRAZENECA, GSK, Allergopharma, allergy therapeutics, Stallergenes, LetiPharma, Roxall, Mundipharma, Chiesi, and alk abelló, outside the submitted work, payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing and/or educational events from Leti Pharma, Alk Abello, Stallergenes, Allergopharma AstraZeneca, Gsk, Mundipharma, Chiesi, and Bial, and support for attending meetings and/or travel from Allergy Therapeutics, Roxall Letipharma, Sanofi, Gsk Stallergenes, Chiesi, and Allergopharma. Mar Gandolfo-Cano has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing and/or educational events from AstraZeneca, Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Leti, Allergy Therapeutics, and Chiesi and support for attending meetings and/or travel from Leti, Inmunotek, Allergy Therapeutics, and Chiesi. Teresa Robledo Echarren has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing and/or educational events from AstraZeneca, GSK, Sanofi, Bial, and Stallergenes, support for attending meetings and/or travel from Diater, Immunotek, and Stallergenes, and participated on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board for Allergy therapeutics and stallergenes. Maria del Mar Moro Moro reports personal fees from SANOFI, ASTRA ZENECA, and GSK, outside the submitted work, has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing and/or educational events from GSK, Astra-Zeneca, Sanofi, Novartis, ALK, and Chiesi, and support for attending meetings and/or travel from Allergy therapeutics, LETI, and ALK. Mª del Mar Reaño Martos has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing and/or educational events from AstraZeneca, GSK, and ALK, support for attending meetings and travel from Allergy therapeutics and payment for expert testimony from Leti and Stallergenes. Rafael Pineda-Pineda reports personal fees from Astra Zeneca, Sanofi, GLAXOSMITHKLINE, and INMUNOTEK, non-financial support from NOVARTIS, LETI, ALLERGY THERAPEUTICS, and DIATER outside the submitted work and has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing and/or educational events, support for attending meetings and/or travel from AstraZeneca, Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Leti, Inmunotek, Diater, Allergy Therapeutics, and Roxall. Marcela Valverde-Monge reports personal fees from GSK and Organon outside the submitted work, has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing and educational events from GSK, and support for attending meetings and travel from Allergy therapeutics. Javier Domínguez-Ortega reports personal fees from ASTRAZENECA, GSK, SANOFI, NOVARTIS, and TEVA, outside the submitted work, has received funding for research and honoraria for consultancy and conferences from AstraZeneca, Chiesi, and GSK, Bial, Novartis, Sanofi, and Teva, and and speaker fees from ALK, LETI Pharma, and Mundipharma. The authors report no other potential conflicts of interest in relation to this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Real-world study in severe eosinophilic asthma patients refractory to anti-IL5 biological agents treated with benralizumab in Spain (ORBE study).BMC Pulm Med. 2021 Dec 18;21(1):417. doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01785-z. BMC Pulm Med. 2021. PMID: 34922515 Free PMC article.
-
Achieving clinical outcomes with benralizumab in severe eosinophilic asthma patients in a real-world setting: orbe II study.Respir Res. 2023 Sep 28;24(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02539-7. Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 37770889 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of benralizumab versus mepolizumab and dupilumab in patients with severe uncontrolled eosinophilic asthma in Spain.J Asthma. 2023 Jun;60(6):1210-1220. doi: 10.1080/02770903.2022.2139718. Epub 2022 Nov 15. J Asthma. 2023. PMID: 36322679
-
Benralizumab, an add-on treatment for severe eosinophilic asthma: evaluation of exacerbations, emergency department visits, lung function, and oral corticosteroid use.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018 Oct 23;14:2059-2068. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S157171. eCollection 2018. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018. PMID: 30425502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of treatment with biologicals (benralizumab, dupilumab, mepolizumab, omalizumab and reslizumab) for severe eosinophilic asthma. A systematic review for the EAACI Guidelines - recommendations on the use of biologicals in severe asthma.Allergy. 2020 May;75(5):1023-1042. doi: 10.1111/all.14221. Epub 2020 Feb 24. Allergy. 2020. PMID: 32034960
Cited by
-
Characteristics and outcomes of patients enrolled in the Connect 360 benralizumab patient support programme in the UK: a retrospective cohort study.BMJ Open Respir Res. 2024 Jan 23;11(1):e001734. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2023-001734. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 38262668 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic literature review of asthma biologic self-administration enhanced by a patient perspective.J Allergy Clin Immunol Glob. 2024 Aug 28;3(4):100334. doi: 10.1016/j.jacig.2024.100334. eCollection 2024 Nov. J Allergy Clin Immunol Glob. 2024. PMID: 39380980 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating large-volume subcutaneous injections of biopharmaceuticals: a systematic review of clinical pipelines and approved products.MAbs. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2402713. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2024.2402713. Epub 2024 Sep 15. MAbs. 2024. PMID: 39279181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bleecker ER, FitzGerald JM, Chanez P, et al. Efficacy and safety of benralizumab for patients with severe asthma uncontrolled with high-dosage inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting beta2-agonists (SIROCCO): a randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2115–2127. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31324-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- FitzGerald JM, Bleecker ER, Nair P, et al. Benralizumab, an anti-interleukin-5 receptor alpha monoclonal antibody, as add-on treatment for patients with severe, uncontrolled, eosinophilic asthma (CALIMA): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2128–2214. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31322-8 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous