The EWAS Catalog: a database of epigenome-wide association studies
- PMID: 35592546
- PMCID: PMC9096146
- DOI: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.17598.2
The EWAS Catalog: a database of epigenome-wide association studies
Abstract
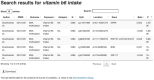
Epigenome-wide association studies (EWAS) seek to quantify associations between traits/exposures and DNA methylation measured at thousands or millions of CpG sites across the genome. In recent years, the increase in availability of DNA methylation measures in population-based cohorts and case-control studies has resulted in a dramatic expansion of the number of EWAS being performed and published. To make this rich source of results more accessible, we have manually curated a database of CpG-trait associations (with p<1x10 -4) from published EWAS, each assaying over 100,000 CpGs in at least 100 individuals. From January 7, 2022, The EWAS Catalog contained 1,737,746 associations from 2,686 EWAS. This includes 1,345,398 associations from 342 peer-reviewed publications. In addition, it also contains summary statistics for 392,348 associations from 427 EWAS, performed on data from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) and the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). The database is accompanied by a web-based tool and R package, giving researchers the opportunity to query EWAS associations quickly and easily, and gain insight into the molecular underpinnings of disease as well as the impact of traits and exposures on the DNA methylome. The EWAS Catalog data extraction team continue to update the database monthly and we encourage any EWAS authors to upload their summary statistics to our website. Details of how to upload data can be found here: http://www.ewascatalog.org/upload. The EWAS Catalog is available at http://www.ewascatalog.org.
Keywords: ALSPAC; EWAS; database; epigenetics; epigenome-wide.
Copyright: © 2022 Battram T et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
- MC_PC_19009/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00011/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_15018/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/S009310/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/4/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/S036520/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00011/4/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00011/5/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G9815508/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

