Temporal trends in the prevalence of metabolically healthy overweight and obesity in Korean youth: data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011-2019
- PMID: 35592898
- PMCID: PMC9260377
- DOI: 10.6065/apem.2142192.096
Temporal trends in the prevalence of metabolically healthy overweight and obesity in Korean youth: data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011-2019
Abstract
Purpose: Metabolically healthy overweight/obesity (MHO) and metabolically unhealthy overweight/obesity (MUO) are distinct clinical phenotypes classified by the presence of cardiometabolic risk factors in an individual. In the present study, we investigated temporal trends in the prevalence of MHO in Korean adolescents using nationally representative data.
Methods: Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011-2019 were used in this study. A total of 5,667 adolescents (3,014 boys, 53.2%) aged 10-18 years was included in this study. MHO was defined as a body mass index ≥85th percentile for the corresponding age and sex and absence of any cardiometabolic risk factors.
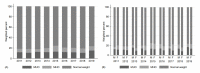
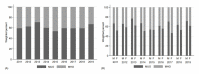
Results: The prevalence of overweight/obesity showed an increasing trend from 18.8% (boys 17.3% and girls 20.6%) in 2011 to 23.7% (boys 24.0% and girls 23.5%) in 2019 (p for trend=0.045). The overall prevalence of MHO during 2011-2019 was 39.2%, which was higher in girls than in boys (boys 33.5%, girls 46.2%, p<0.001), and the change in prevalence of MHO from 2011 to 2019 (from 34.8% to 35.7%) was not significant. Among MUO, the most prevalent cardiometabolic risk factor was dysglycemia (48.8%), followed by elevated blood pressure (41.5%), low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (35.0%), and high triglycerides (29.7%).
Conclusion: We observed a high prevalence of MHO in Korean youth with overweight/obesity. Although the prevalence of overweight/obesity increased, the prevalence of MHO was stable during 2011-2019. A risk-stratified approach based on metabolic health status can help reducing the medical and socioeconomic costs associated with obesity treatment.
Keywords: Adolescent; Child; Metabolically benign; Obesity; Overweight; Pediatric obesity; Prevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Abarca-Gómez L, Abdeen ZA, Hamid ZA, Abu-Rmeileh NM, Acosta-Cazares B, Acuin C, et al. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet. 2017;390:2627–42. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Steinberger J, Daniels SR, Eckel RH, Hayman L, Lustig RH, McCrindle B, et al. Progress and challenges in metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Atherosclerosis, Hypertension, and Obesity in the Young Committee of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; and Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Circulation. 2009;119:628–47. - PubMed
-
- Singh AS, Mulder C, Twisk JW, Van Mechelen W, Chinapaw MJ. Tracking of childhood overweight into adulthood: a systematic review of the literature. Obes Rev. 2008;9:474–88. - PubMed
-
- Park MH, Falconer C, Viner RM, Kinra S. The impact of childhood obesity on morbidity and mortality in adulthood: a systematic review. Obes Rev. 2012;13:985–1000. - PubMed
-
- Prince RL, Kuk JL, Ambler KA, Dhaliwal J, Ball GD. Predictors of metabolically healthy obesity in children. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:1462–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

