PD-L1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma: A key biomarker from the laboratory to the bedside
- PMID: 35593124
- PMCID: PMC9209791
- DOI: 10.1002/cre2.590
PD-L1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma: A key biomarker from the laboratory to the bedside
Abstract
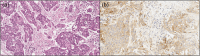
Objectives and background: Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is a highly malignant disease with an increasing incidence. The need to improve therapeutic strategies for patients affected by OSCC is an urgent challenge. Currently, the advent of immunotherapy represents an important step toward this aim. Programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), a membrane protein that can be expressed on tumor and inflammatory cells is a key biomarker whose expression is determined by means of immunohistochemistry and is necessary for selecting patients for immunotherapy.
Methods: In this study, we review the methods of PD-L1 assessment and outcomes achieved with immunotherapy in the treatment of OSCC patients.
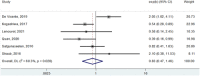
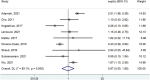
Results: Based on a meta-analysis we demonstrate a lack of prognostic significance of PD-L1 in OSCC.
Conclusions: We also highlight unresolved issues including difficulties in standardizing PD-L1 evaluation and discuss future opportunities such as leveraging digital pathology.
Keywords: CD274; PD-L1; meta-analysis; oral cancer; oral squamous cell carcinoma; programmed death-ligand 1.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical and Experimental Dental Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adamski, Ł. J. , Starzyńska, A. , Adamska, P. , Kunc, M. , Sakowicz‐Burkiewicz, M. , Marvaso, G. , Alterio, D. , Korwat, A. , Jereczek‐Fossa, B. A. , & Pęksa, R. (2021). High PD‐L1 expression on tumor cells indicates worse overall survival in advanced oral squamous cell carcinomas of the tongue and the floor of the mouth but not in other oral compartments. Biomedicines, 9, 1132. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burtness, B. , Harrington, K. J. , Greil, R. , Soulières, D. , Tahara, M. , de Castro, G. Jr , Psyrri, A. , Basté, N. , Neupane, P. , Bratland, Å. , Fuereder, T. , Hughes, B. , Mesía, R. , Ngamphaiboon, N. , Rordorf, T. , Wan Ishak, W. Z. , Hong, R. L. , González Mendoza, R. , Roy, A. , … KEYNOTE‐048 Investigators . (2019). Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE‐048): A randomised, open‐label, phase 3 study. Lancet, 394, 1915–1928. - PubMed
-
- Cerbelli, B. , Girolami, I. , Eccher, A. , Costarelli, L. , Taccogna, S. , Scialpi, R. , Benevolo, M. , Lucante, T. , Luigi Alò, P. , Stella, F. , Gemma Pignataro, M. , Fadda, G. , Perrone, G. , D'Amati, G. , & Martini, M. (2021). Evaluating PD‐L1 in head & neck squamous cell carcinoma: Concordance between 22C3 PharmaDx and SP263 assays on whole sections from a multicenter study. Histopathology, 80(2), 397–406. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen, X. J. , Tan, Y. Q. , Zhang, N. , He, M. J. , & Zhou, G. (2019). Expression of programmed cell death‐ligand 1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma and oral leukoplakia is associated with disease progress and CD8+ tumor‐infiltrating lymphocytes. Pathology Research and Practice, 215, 152418. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

