Immunogenicity, safety, and antiphospholipid antibodies after SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome
- PMID: 35593174
- PMCID: PMC9127455
- DOI: 10.1177/09612033221102073
Immunogenicity, safety, and antiphospholipid antibodies after SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome
Abstract
Objective: Coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) has an increased risk of coagulopathy with high frequency of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL). Recent reports of thrombosis associated with adenovirus-based vaccines raised concern that SARS-CoV-2 immunization in primary antiphospholipid syndrome (PAPS) patients may trigger clotting complications. Our objectives were to assess immunogenicity, safety, and aPL production in PAPS patients, after vaccinating with Sinovac-CoronaVac, an inactivated virus vaccine against COVID-19.
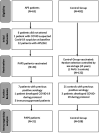
Methods: This prospective controlled phase-4 study of PAPS patients and a control group (CG) consisted of a two-dose Sinovac-CoronaVac (D0/D28) and blood collection before vaccination (D0), at D28 and 6 weeks after second dose (D69) for immunogenicity/aPL levels. Outcomes were seroconversion (SC) rates of anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1/S2 IgG and/or neutralizing antibodies (NAb) at D28/D69 in naïve participants. Safety and aPL production were also assessed.
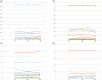
Results: We included 44 PAPS patients (31 naïve) and 132 CG (108 naïve) with comparable age (p=0.982) and sex (p>0.999). At D69, both groups had high and comparable SC (83.9% vs. 93.5%, p=0.092), as well as NAb positivity (77.4% vs. 78.7%, p=0.440), and NAb-activity (64.3% vs. 60.9%, p=0.689). Thrombotic events up to 6 months or other moderate/severe side effects were not observed. PAPS patients remained with stable aPL levels throughout the study at D0 vs. D28 vs. D69: anticardiolipin (aCL) IgG (p=0.058) and IgM (p=0.091); anti-beta-2 glycoprotein I (aβ2GPI) IgG (p=0.513) and IgM (p=0.468).
Conclusion: We provided novel evidence that Sinovac-CoronaVac has high immunogenicity and safety profile in PAPS. Furthermore, Sinovac-CoronaVac did not trigger thrombosis nor induced changes in aPL production.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2 vaccine; antiphospholipid antibodies; antiphospholipid syndrome; vaccine immunogenicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic autoimmune myopathies: a prospective phase 4 controlled trial of an inactivated virus vaccine against SARS-CoV-2.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022 Aug 3;61(8):3351-3361. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab773. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022. PMID: 34664616 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in primary Sjögren's syndrome: humoral response, safety, and effects on disease activity.Clin Rheumatol. 2022 Jul;41(7):2079-2089. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06134-x. Epub 2022 Mar 19. Clin Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35306594 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of Distinct Therapies on Antibody Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2022 Apr;74(4):562-571. doi: 10.1002/acr.24824. Epub 2022 Mar 4. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2022. PMID: 34806342 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
CoronaVac: A review of efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of the inactivated vaccine against SARS-CoV-2.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022 Nov 30;18(6):2096970. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2096970. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022. PMID: 35878789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 and Antiphospholipid Antibodies: Time for a Reality Check?Semin Thromb Hemost. 2022 Feb;48(1):72-92. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1728832. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2022. PMID: 34130340 Review.
Cited by
-
Growing attention of immunogenicity among patients with autoimmune diseases post-SARS-CoV-2 vaccination: meta-analysis and systematic reviews of the current studies.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2478319. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2478319. Epub 2025 Mar 26. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 40135763 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal efficacy and toxicity of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in cancer patients treated with immunotherapy.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Jan 20;14(1):49. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05548-4. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 36670100 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and tolerance of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection in systemic lupus erythematosus: results from the COVAD study.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023 Jul 5;62(7):2453-2463. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac661. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023. PMID: 36413073 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Vaccines and Autoimmune Hematologic Disorders.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jun 16;10(6):961. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10060961. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35746569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Co-Infections to Autoimmune Disease via Hyperactivated Innate Immunity: COVID-19 Autoimmune Coagulopathies, Autoimmune Myocarditis and Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 3;24(3):3001. doi: 10.3390/ijms24033001. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769320 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Levi M, van der Poll T. Inflammation and coagulation. Crit Care Med 2010; 38(2 Suppl): S26–S34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

