The barriers and facilitators to satisfaction with botulinum neurotoxin treatment in people with cervical dystonia: a systematic review
- PMID: 35593979
- PMCID: PMC9349125
- DOI: 10.1007/s10072-022-06114-8
The barriers and facilitators to satisfaction with botulinum neurotoxin treatment in people with cervical dystonia: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Cervical dystonia (CD) is an isolated, focal, idiopathic dystonia affecting the neck and upper back. CD is usually treated by botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) injections into the dystonic muscles; however, about 20% of people will discontinue BoNT therapy. This systematic review aimed to determine the barriers to satisfaction and facilitators that could improve satisfaction with BoNT therapy for people with CD.
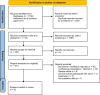
Methods: A database search for journal articles investigating satisfaction with BoNT treatment in CD identified seven qualitative studies and one randomised controlled trial. Results were grouped into "direct" and "indirect" barriers and facilitators.
Results: The most reported direct barrier to satisfaction with BoNT was treatment non-response, reported by up to 66% of participants. Other direct barriers included negative side effects, early wearing-off of treatment effect and inexperience of the treating physician. Indirect barriers included limited accessibility to treatment (including cost) and personal choice. Direct facilitators of satisfaction with BoNT included relief of symptoms and flexible re-treatment intervals. Indirect facilitators included easy accessibility to treatment.
Conclusions: Despite BoNT having a discontinuation rate of only 20%, it appears a much greater proportion of people with CD are dissatisfied with this treatment. As BoNT is currently the main treatment offered to people with CD, efforts to improve treatment response rates, reduce side effects and make treatment more flexible and readily available should be adopted to improve the quality of life for people with CD.
Keywords: Barriers; Botulinum toxin; Cervical dystonia; Facilitators; Satisfaction.
© 2022. Crown.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
-
- Fahn S, Marsden CD, Calne DB. Classification and investigation of dystonia. In: Marsden CD, editor. Movement Disorders 2. London: Butterworth; 1987. pp. 332–352.
-
- Jahanshahi M, Marsden CD (1990) A longitudinal follow-up study of depression, disability, and body concept in torticollis. Behav Neurol 3(4).:10.3233/ben-1990-3403 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials