The vulnerability of maintenance dialysis patients with COVID-19: mortality and risk factors from a developing country
- PMID: 35594312
- PMCID: PMC9132419
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2075914
The vulnerability of maintenance dialysis patients with COVID-19: mortality and risk factors from a developing country
Abstract
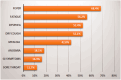
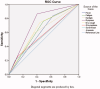
Patients on maintenance dialysis therapy are especially vulnerable to COVID-19 and its complications. This study aimed to assess the incidence, epidemiological characteristics, and mortality rate of COVID-19 among maintenance dialysis patients. This retrospective observational chart review study included 548 patients from all dialysis units in the West Bank of Palestine who acquired COVID-19 between 5 March 2020, and 11 August 2021. We collected data on patients' demographics, clinical features, and outcomes. A multivariable logistic regression model was used to assess independent risk factors for COVID-19-related mortality. The incidence of COVID-19 among maintenance dialysis patients was 35.3%, as 548 out of 1554 patients have tested positive during the study period. Patients on haemodialysis were three times riskier to get infected than those on peritoneal dialysis (37% vs 11.3%). Half (50.2%) of infected patients required hospitalisation, and 24.5% were admitted to an intensive care unit, while the mortality rate stood at 26.8%. Old age, male sex, central venous catheter use, comorbid diabetes, smoking, and having an RH negative blood group type were determined to be significantly associated with increased risk of mortality. In conclusion, the incidence of COVID-19 among Palestinian maintenance dialysis patients was notably high, especially among haemodialysis patients. High rates of hospitalisation, ICU admission, intubation and death were observed, and predictive factors for COVID-19-related mortality were identified. Therefore, the implementation of strict infection control measures and promotion of home dialysis are warranted to reduce the infection rate.KEY MESSAGESThe incidence of COVID-19 among Palestinian maintenance dialysis patients was notably high; more than one-third of the total dialysis population acquired COVID-19, with haemodialysis patients being three times more likely to get infected compared to their peritoneal dialysis counterparts.The mortality rate among maintenance dialysis patients was 26.8%, more than 25 times higher than that of the general population. The risk of mortality was significantly increased with age, male sex, smoking, diabetes, and having central venous catheter as vascular access for haemodialysis.Strict infection control measures, as well as the promotion of home dialysis, are necessary to reduce the risk of infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; haemodialysis; incidence; mortality rate; peritoneal dialysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report there are no competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM.. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Jama. 2020;323(13):1239–1242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical