Symptom-Based Cluster Analysis Categorizes Sjögren's Disease Subtypes: An International Cohort Study Highlighting Disease Severity and Treatment Discordance
- PMID: 35594474
- PMCID: PMC9427679
- DOI: 10.1002/art.42238
Symptom-Based Cluster Analysis Categorizes Sjögren's Disease Subtypes: An International Cohort Study Highlighting Disease Severity and Treatment Discordance
Abstract
Objective: Although symptom relief is a critical aspect for successful drug development in Sjögren's disease, patient experiences with Sjögren's-related symptoms are understudied. Our objective was to determine how pain, dryness, and fatigue, the cardinal symptoms of Sjögren's disease, drive cluster phenotypes.
Methods: We used data from the Sjögren's International Collaborative Clinical Alliance (SICCA) Registry and a Sjögren's Foundation survey. We performed hierarchical clustering of symptoms by levels of dryness, fatigue, and pain. Using international and US cohorts, we performed multiple logistic regression analysis to compare the clusters, which included comparisons of differences in symptoms, quality of life (QoL), medication use, and systemic manifestations.
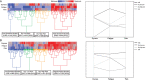
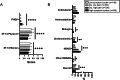
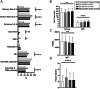
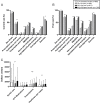
Results: Four similar clusters were identified among 1,454 SICCA registrants and 2,920 Sjögren's Foundation survey participants: 1) low symptom burden in all categories (LSB); 2) dry with low pain and low fatigue (DLP); 3) dry with high pain and low to moderate fatigue (DHP); and 4) high symptom burden in all categories (HSB). Distribution of SICCA registrants matching the symptom profile for each cluster was 10% in the LSB cluster, 30% in the DLP cluster, 23% in the DHP cluster, and 37% in the HSB cluster. Distribution of survey participants matching the symptom profile for each cluster was 23% in the LSB cluster, 14% in the DLP cluster, 21% in the DHP cluster, and 42% in the HSB cluster. Individuals in the HSB cluster had more total symptoms and lower QoL but lower disease severity than those in the other clusters. Despite having milder disease as measured by laboratory tests and organ involvement, individuals in the HSB cluster received immunomodulatory treatment most often.
Conclusion: We identified 4 symptom-based Sjögren's clusters and showed that symptom burden and immunomodulatory medication use do not correlate with Sjögren's end-organ or laboratory abnormalities. Findings highlight a discordance between objective measures and treatments and offer updates to proposed symptom-based clustering approaches.
© 2022 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American College of Rheumatology.
Conflict of interest statement
Author disclosures are available at
Figures
References
-
- Meijer JM, Meiners PM, Huddleston Slater JJ, Spijkervet FK, Kallenberg CG, Vissink A, et al. Health‐related quality of life, employment and disability in patients with Sjogren's syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2009;489:1077–82. - PubMed
-
- Fox RI, Fox CM. Sjögren syndrome: why do clinical trials fail? Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2016;423:519–30. - PubMed
-
- Alarcón GS, McGwin G Jr, Brooks K, Roseman JM, Fessler BJ, Sanchez ML, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus in three ethnic groups. XI. Sources of discrepancy in perception of disease activity: a comparison of physician and patient visual analog scale scores. Arthritis Rheum 2002;474:408–13. - PubMed
-
- Pisetsky DS, Clowse ME, Criscione‐Schreiber LG, Rogers JL. A novel system to categorize the symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus [review]. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2019;716:735–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

