Identification and development of a series of disubstituted piperazines for the treatment of Chagas disease
- PMID: 35594652
- PMCID: PMC11458808
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114421
Identification and development of a series of disubstituted piperazines for the treatment of Chagas disease
Abstract
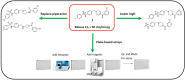
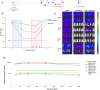
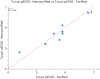
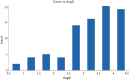
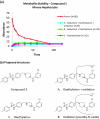
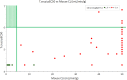
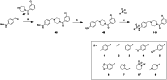
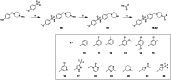
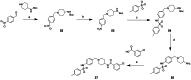
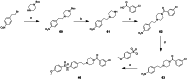
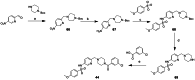
Approximately 6-7 million people around the world are estimated to be infected with Trypanosoma cruzi, the causative agent of Chagas disease. The current treatments are inadequate and therefore new medical interventions are urgently needed. In this paper we describe the identification of a series of disubstituted piperazines which shows good potency against the target parasite but is hampered by poor metabolic stability. We outline the strategies used to mitigate this issue such as lowering logD, bioisosteric replacements of the metabolically labile piperazine ring and use of plate-based arrays for quick diversity scoping. We discuss the success of these strategies within the context of this series and highlight the challenges faced in phenotypic programs when attempting to improve the pharmacokinetic profile of compounds whilst maintaining potency against the desired target.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

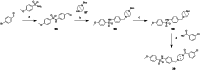
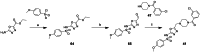
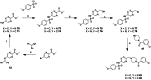
References
-
- Kratz J.M. Drug discovery for chagas disease: a viewpoint. Acta Trop. 2019:105107. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

