The interaction of spongistatin 1 with tubulin
- PMID: 35594923
- PMCID: PMC10062379
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2022.109296
The interaction of spongistatin 1 with tubulin
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "The interaction of spongistatin 1 with tubulin" [Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 727 (2022) 109296 (7 pages)].Arch Biochem Biophys. 2022 Nov 15;730:109412. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2022.109412. Epub 2022 Sep 26. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2022. PMID: 36175266 No abstract available.
Abstract
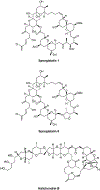
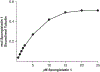
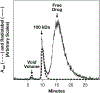
A tritiated derivative of the sponge-derived natural product spongistatin 1 was prepared, and its interactions with tubulin were examined. [3H]Spongistatin 1 was found to bind rapidly to tubulin at a single site (the low specific activity of the [3H]spongistatin 1, 0.75 Ci/mmol, prevented our defining an association rate), and the inability of spongistatin 1 to cause an aberrant assembly reaction was confirmed. Spongistatin 1 bound to tubulin very tightly, and we could detect no significant dissociation reaction from tubulin. The tubulin-[3H]spongistatin 1 complex did dissociate in 8 M urea, so there was no evidence for covalent bond formation. Apparent KD values were obtained by Scatchard analysis of binding data and by Hummel-Dreyer chromatography (3.5 and 1.1 μM, respectively). The effects of a large cohort of vinca domain drugs on the binding of [3H]spongistatin 1 to tubulin were evaluated. Compounds that did not cause aberrant assembly reactions (halichondrin B, eribulin, maytansine, and rhizoxin) caused little inhibition of [3H]spongistatin 1 binding. Little inhibition also occurred with the peptides dolastatin 15, its active pentapeptide derivative, vitilevuamide, or diazonamide A, nor with the vinca alkaloid vinblastine. Strong inhibition was observed with dolastatin 10, hemiasterlin, and cryptophycin 1, all of which cause aberrant assembly reactions that might actually mask the spongistatin 1 binding site. Spongistatin 5 was found to be a competitive inhibitor of [3H]spongistatin 1 binding, with an apparent Ki of 2.2 μM. We propose that the strong picomolar cytotoxicity of spongistatin 1 probably derives from its extremely tight binding to tubulin.
Keywords: HPLC Hummel-Dreyer analysis; Halichondrin B; Inhibitors of microtubule assembly; Spongistatin 1; Spongistatin 5; Vinca domain.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Bai R, Pettit GR, Hamel E, Binding of dolastatin 10 to tubulin at a distinct site for peptide antimitotic agents near the exchangeable nucleotide and vinca alkaloid sites, J. Biol. Chem 265 (1990) 17141–17149. - PubMed
-
- Bai R, Durso NA, Sackett DL, Hamel E, Interactions of the sponge-derived antimitotic tripeptide hemiasterlin with tubulin: comparison with dolastatin 10 and cryptophycin 1, Biochemistry 38 (1999) 14301–14310. - PubMed
-
- Bai R, Schwartz R, Kepler JA, Pettit GR, Hamel E, Characterization of the interaction of cryptophycin 1 with tubulin: binding in the vinca domain, competitive inhibition of dolastatin 10 binding, and an unusual aggregation reaction, Cancer Res. 56 (1996) 4398–4406. - PubMed
-
- Edler MC, Fernandez AM, Lassota P, Ireland C, Barrows LR, Inhibition of tubulin polymerization by vitilevuamide, a bicyclic marine peptide, at a site distinct from colchicine, the vinca alkaloids, and dolastatin 10, Biochem. Pharmacol 63 (2002) 707–715. - PubMed
-
- Khalil MW, Sasse F, Lunsdorf H, Elnakady YA, Reichenbach H, Mechanism of action of tubulysin, an antimitotic peptide from myxobacteria, Chembiochem 7 (2006) 678–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

