RNA2Immune: A Database of Experimentally Supported Data Linking Non-coding RNA Regulation to The Immune System
- PMID: 35595213
- PMCID: PMC10626051
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gpb.2022.05.001
RNA2Immune: A Database of Experimentally Supported Data Linking Non-coding RNA Regulation to The Immune System
Abstract
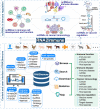
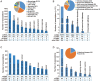
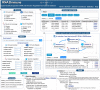
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), such as microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs), have emerged as important regulators of the immune system and are involved in the control of immune cell biology, disease pathogenesis, as well as vaccine responses. A repository of ncRNA-immune associations will facilitate our understanding of ncRNA-dependent mechanisms in the immune system and advance the development of therapeutics and prevention for immune disorders. Here, we describe a comprehensive database, RNA2Immune, which aims to provide a high-quality resource of experimentally supported database linking ncRNA regulatory mechanisms to immune cell function, immune disease, cancer immunology, and vaccines. The current version of RNA2Immune documents 50,433 immune-ncRNA associations in 42 host species, including (1) 6690 ncRNA associations with immune functions involving 31 immune cell types; (2) 38,672 ncRNA associations with 348 immune diseases; (3) 4833 ncRNA associations with cancer immunology; and (4) 238 ncRNA associations with vaccine responses involving 26 vaccine types targeting 22 diseases. RNA2Immune provides a user-friendly interface for browsing, searching, and downloading ncRNA-immune system associations. Collectively, RNA2Immune provides important information about how ncRNAs influence immune cell function, how dysregulation of these ncRNAs leads to pathological consequences (immune diseases and cancers), and how ncRNAs affect immune responses to vaccines. RNA2Immune is available at http://bio-bigdata.hrbmu.edu.cn/rna2immune/home.jsp.
Keywords: Cancer immunology; Immune cell; Immune disease; Vaccine; ncRNA.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ncR2Met (lncR2metasta v2.0): An updated database for experimentally supported ncRNAs during cancer metastatic events.Genomics. 2023 Mar;115(2):110569. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2023.110569. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36736440
-
Comprehensive analysis of ncRNA involvement in brain microglia immunology.Clin Immunol. 2022 Aug;241:109075. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2022.109075. Epub 2022 Jul 6. Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35809855
-
ncFO: A Comprehensive Resource of Curated and Predicted ncRNAs Associated with Ferroptosis.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2023 Apr;21(2):278-282. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2022.09.004. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 36162726 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Coding RNAs in Neurological and Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Unraveling the Hidden Players in Disease Pathogenesis.Cells. 2024 Jun 19;13(12):1063. doi: 10.3390/cells13121063. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38920691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs and leaf senescence: Small molecules with important roles.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024 Feb;207:108399. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2024.108399. Epub 2024 Jan 23. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38277833 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs in Cancer and Cardiovascular Disease.Cells. 2022 Nov 10;11(22):3551. doi: 10.3390/cells11223551. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36428980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-Coding RNAs and Innate Immune Responses in Cancer.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 11;12(9):2072. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12092072. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-Coding RNA in Tumor Cells and Tumor-Associated Myeloid Cells-Function and Therapeutic Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 2;25(13):7275. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137275. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNASNP-v4: a comprehensive database for miRNA-related SNPs across 17 species.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 6;53(D1):D1066-D1074. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae888. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39413204 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the Non-coding: Tools and Databases Unveiling the Hidden World of "Junk" RNAs for Innovative Therapeutic Exploration.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Jun 7;7(7):1901-1915. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00388. eCollection 2024 Jul 12. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39022352 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xiao C., Rajewsky K. MicroRNA control in the immune system: basic principles. Cell. 2009;136:26–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

