Breakthroughs in hepatitis C research: from discovery to cure
- PMID: 35595834
- PMCID: PMC9122245
- DOI: 10.1038/s41575-022-00608-8
Breakthroughs in hepatitis C research: from discovery to cure
Abstract
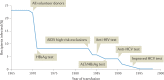
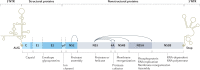
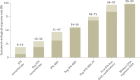
In the 1970s, an unknown virus was suspected for documented cases of transfusion-associated hepatitis, a phenomenon called non-A, non-B hepatitis. In 1989, the infectious transmissible agent was identified and named hepatitis C virus (HCV) and, soon enough, the first diagnostic HCV antibody test was developed, which led to a dramatic decrease in new infections. Today, HCV infection remains a global health burden and a major cause of liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma and liver transplantation. However, tremendous advances have been made over the decades, and HCV became the first curable, chronic viral infection. The introduction of direct antiviral agents revolutionized antiviral treatment, leading to viral eradication in more than 98% of all patients infected with HCV. This Perspective discusses the history of HCV research, which reads like a role model for successful translational research: starting from a clinical observation, specific therapeutic agents were developed, which finally were implemented in national and global elimination programmes.
© 2022. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
M.P.M. received speaker and/or consulting fees and/or grant or research support from AbbVie, BMS, Gilead, Merck/MSD and Janssen. B.M. received speaker and/or consulting fees from Abbott Molecular, Astellas, Intercept, Falk, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Fujirebio, Janssen-Cilag, Merck/MSD and Roche. He also received research support from Abbott Molecular and Roche.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Hepatitis Report. WHOhttps://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/255016/9789?sequence=1 (2017).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

