Effect of osmotic stress on live cell plasma membranes, probed via Laurdan general polarization measurements
- PMID: 35596525
- PMCID: PMC9279170
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.05.016
Effect of osmotic stress on live cell plasma membranes, probed via Laurdan general polarization measurements
Abstract
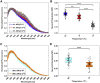
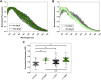
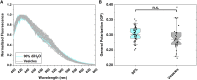
Here we seek to gain insight into changes in the plasma membrane of live cells upon the application of osmotic stress using Laurdan, a fluorescent probe that reports on membrane organization, hydration, and dynamics. It is known that the application of osmotic stress to lipid vesicles causes a decrease in Laurdan's generalized polarization (GP), which has been interpreted as an indication of membrane stretching. In cells, we see the opposite effects, as GP increases when the osmolarity of the solution is decreased. This increase in GP is associated with the presence of caveolae, which are known to disassemble and flatten in response to osmotic stress.
Copyright © 2022 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

