Micro-Gel Ensembles for Accelerated Healing of Chronic Wound via pH Regulation
- PMID: 35596608
- PMCID: PMC9353480
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202201254
Micro-Gel Ensembles for Accelerated Healing of Chronic Wound via pH Regulation
Abstract
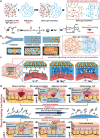
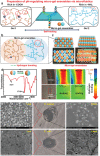
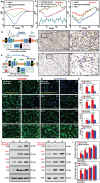
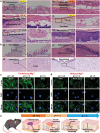
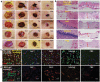
The pH value in the wound milieu plays a key role in cellular processes and cell cycle processes involved in the process of wound healing. Here, a microfluidic assembly technique is employed to fabricate micro-gel ensembles that can precisely tune the pH value of wound surface and accelerate wound healing. The micro-gel ensembles consist of poly (hydroxypropyl acrylate-co-acrylic acid)-magnesium ions (poly-(HPA-co-AA)-Mg2+ ) gel and carboxymethyl chitosan (CMCS) gel, which can release and absorb hydrogen ion (H+ ) separately at different stages of healing in response to the evolution of wound microenvironment. By regulating the wound pH to affect the proliferation and migration of cell on the wound and the activity of various biological factors in the wound, the physiological processes are greatly facilitated which results in much accelerated healing of chronic wound. This work presents an effective strategy in designing wound healing materials with vast potentials for chronic wound management.
Keywords: accelerated wound healing; chronic wound; micro-gel ensembles; microfluidic assembly; wound pH regulation.
© 2022 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gurtner G. C., Werner S., Barrandon Y., Longaker M. T., Nature 2008, 453, 314. - PubMed
-
- Mao C., Xiang Y., Liu X., Cui Z., Yang X., Li Z., Zhu S., Zheng Y., Yeung K. W. K., Wu S., ACS Nano 2018, 12, 1747. - PubMed
-
- Martin P., Science 1997, 276, 75. - PubMed
-
- Tan Q.‐W., Tang S.‐L., Zhang Y., Yang J.‐Q., Wang Z.‐L., Xie H.‐Q., Lv Q., J. Invest. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
