A Small Molecule Selected from a DNA-Encoded Library of Natural Products That Binds to TNF-α and Attenuates Inflammation In Vivo
- PMID: 35596609
- PMCID: PMC9313502
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202201258
A Small Molecule Selected from a DNA-Encoded Library of Natural Products That Binds to TNF-α and Attenuates Inflammation In Vivo
Abstract
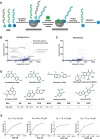
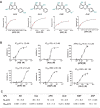
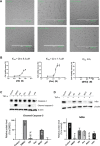
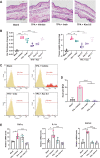
Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) inhibitors have shown great success in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. However, to date, approved drugs targeting TNF-α are restricted to biological macromolecules, largely due to the difficulties in using small molecules for pharmaceutical intervention of protein-protein interactions. Herein the power of a natural product-enriched DNA-encoded library (nDEL) is exploited to identify small molecules that interfere with the protein-protein interaction between TNF-α and the cognate receptor. Initially, to select molecules capable of binding to TNF-α , "late-stage" DNA modification method is applied to construct an nDEL library consisted of 400 sterically diverse natural products and pharmaceutically active chemicals. Several natural products, including kaempferol, identified not only show direct interaction with TNF-α, but also lead to the blockage of TNF-α/TNFR1 interaction. Significantly, kaempferol attenuates the TNF-α signaling in cells and reduces the 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetateinduced ear inflammation in mice. Structure-activity-relationship analyses demonstrate the importance of substitution groups at C-3, C-7, and C-4' of kaempferol. The nDEL hit, kaempferol, represents a novel chemical scaffold capable of specifically recognizing TNF-α and blocking its signal transduction, a promising starting point for the development of a small molecule TNF-α inhibitor for use in the clinical setting.
Keywords: DNA-encoded library; flavonoid; inflammation; kaempferol; tumor necrosis factor α.
© 2022 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) inhibitors from small molecule library screening for their therapeutic activity profiles against rheumatoid arthritis using target-driven approaches and binary QSAR models.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2019 Jun;37(9):2464-2476. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2018.1491423. Epub 2018 Dec 23. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2019. PMID: 30047845
-
Effect of apigenin, kaempferol and resveratrol on the gene expression and protein secretion of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-10 (IL-10) in RAW-264.7 macrophages.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Sep;93:1205-1212. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.07.054. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28738536
-
Flavonoids inhibit tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced up-regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in respiratory epithelial cells through activator protein-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB: structure-activity relationships.Mol Pharmacol. 2004 Sep;66(3):683-93. doi: 10.1124/mol.66.3.. Mol Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15322261
-
TNF-α inhibitors with anti-oxidative stress activity from natural products.Curr Top Med Chem. 2012;12(13):1408-21. doi: 10.2174/156802612801784434. Curr Top Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22650374 Review.
-
Modulating TNF-alpha signaling with natural products.Drug Discov Today. 2006 Aug;11(15-16):725-32. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2006.06.002. Drug Discov Today. 2006. PMID: 16846800 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential mechanism of ginseng in the treatment of periodontitis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Apr 1;42(2):181-191. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2024.2023285. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38597078 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Research advances of Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim. polyphenols in inflammatory diseases.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 26;15:1305886. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1305886. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38343532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An orally available small molecule that targets soluble TNF to deliver anti-TNF biologic-like efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 16;13:1037983. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1037983. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36467083 Free PMC article.
-
Metal-Free and Open-Air Arylation Reactions of Diaryliodonium Salts for DNA-Encoded Library Synthesis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Sep;9(26):e2202790. doi: 10.1002/advs.202202790. Epub 2022 Jul 19. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 35853237 Free PMC article.
-
Encoding and display technologies for combinatorial libraries in drug discovery: The coming of age from biology to therapy.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Aug;14(8):3362-3384. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.04.006. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39220863 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- a) Xu H., Ma F., Wang N., Hou W., Xiong H., Lu F., Li J., Wang S., Ma P., Yang G., Lerner R. A., Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901551; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Xu H., Gu Y., Zhang S., Xiong H., Ma F., Lu F., Ji Q., Liu L., Ma P., Hou W., Yang G., Lerner R. A., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 13273; - PubMed
- c) Wang X., Liu J., Yan Z., Liu X., Liu S., Suo Y., Lu W., Yue J., Chen K., Jiang H., Zhao Y., Zheng M., Dai D., Lu X., Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 2841; - PMC - PubMed
- d) Gao H., Lin S., Zhang S. N., Chen W. J., Liu X. W., Yang G., Lerner R. A., Xu H. T., Zhou Z., Yi W., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 1959; - PubMed
- e) Xiong H., Gu Y., Zhang S. N., Lu F. P., Ji Q., Liu L. L., Ma P. X., Yang G., Hou W., Xu H. T., Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 4692; - PubMed
- f) Potowski M., Luttig R., Vakalopoulos A., Brunschweiger A., Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 5480; - PubMed
- g) Zhang J., Li X. F., Wei H. M., Li Y. F., Zhang G., Li Y. Z., Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 8429; - PubMed
- h) Ma F., Li J., Zhang S., Gu Y., Tan T., Chen W., Wang S., Xu H., Yang G., Lerner R. A., ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 1639;
- i) Gerry C., Wawer M., Clemons P., Schreiber S., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 10225. - PMC - PubMed
-
- a) Cai B., Kim D., Akhand S., Sun Y., Cassell R. J., Alpsoy A., Dykhuizen E. C., Rijn R. M. V., Wendt M. K., Krusemark C. J., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 17057; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Deng Y., Peng J., Xiong F., Song Y., Zhou Y., Zhang J., Lam F. S., Xie C., Shen W., Huang Y., Meng L., Li X., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 14965; - PubMed
- c) Huang Y., Meng L., Nie Q., Zhou Y., Chen L., Yang S., Fung Y. M. E., Li X., Huang C., Cao Y., Li Y., Li X., Nat. Chem. 2021, 13, 77. - PubMed
-
- a) Belyanskaya S. L., Ding Y., Callahan J. F., Lazaar A. L., Israel D. I., Chembiochem. 2017, 18, 837; - PubMed
- b) Harris P. A., King B. W., Bandyopadhyay D., Berger S. B., Campobasso N., Capriotti C. A., Cox J. A., Dare L., Dong X., Finger J. N., Grady L. C., Hoffman S. J., Jeong J. U., Kang J., Kasparcova V., Lakdawala A. S., Lehr R., McNulty D. E., Nagilla R., Ouellette M. T., Pao C. S., Rendina A. R., Schaeffer M. C., Summerfield J. D., Swift B. A., Totoritis R. D., Ward P., Zhang A., Zhang D., Marquis R. W., J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 2163. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
