Usefulness of lung ultrasound for early detection of hospital-acquired pneumonia in cardiac critically ill patients on venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- PMID: 35596817
- PMCID: PMC9124275
- DOI: 10.1186/s13613-022-01013-9
Usefulness of lung ultrasound for early detection of hospital-acquired pneumonia in cardiac critically ill patients on venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
Abstract
Background: Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) is the most common and severe complication in patients treated with venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA ECMO) and its diagnosis remains challenging. Nothing is known about the usefulness of lung ultrasound (LUS) in early detection of HAP in patients treated with VA ECMO. Also, LUS and chest radiography were performed when HAP was suspected in cardiac critically ill adult VA ECMO presenting with acute respiratory failure. The sonographic features of HAP in VA ECMO patients were determined and we assessed the performance of the lung ultrasound simplified clinical pulmonary score (LUS-sCPIS), the sCPIS and bioclinical parameters or chest radiography alone for early diagnosis of HAP.
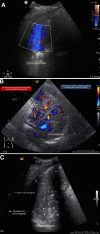
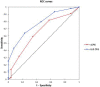
Results: We included 70 patients, of which 44 (63%) were independently diagnosed with HAP. LUS examination revealed that color Doppler intrapulmonary flow (P = 0.0000043) and dynamic air bronchogram (P = 0.00024) were the most frequent HAP-related signs. The LUS-sCPIS (area under the curve = 0.77) yielded significantly better results than the sCPIS (area under the curve = 0.65; P = 0.004), while leukocyte count, temperature and chest radiography were not discriminating for HAP diagnosis.
Discussion: Diagnosis of HAP is a daily challenge for the clinician managing patients on venoarterial ECMO. Lung ultrasound can be a valuable tool as the initial imaging modality for the diagnosis of pneumonia. Color Doppler intrapulmonary flow and dynamic air bronchogram appear to be particularly insightful for the diagnosis of HAP.
Keywords: Color Doppler intrapulmonary flow; Doppler color lung ultrasound; Dynamic air bronchogram; Hospital-acquired pneumonia; Intensive care unit; Lung ultrasound; Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Alba AC, Foroutan F, Buchan TA, Alvarez J, Kinsella A, Clark K, et al. Mortality in patients with cardiogenic shock supported with VA ECMO: a systematic review and meta-analysis evaluating the impact of etiology on 29,289 patients. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2021;40:260–268. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2021.01.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bouglé A, Bombled C, Margetis D, Lebreton G, Vidal C, Coroir M, et al. Ventilator-associated pneumonia in patients assisted by veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support: epidemiology and risk factors of treatment failure. PLoS ONE. 2018;13:e0194976. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194976. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

