Necroptosis in heart disease: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- PMID: 35597275
- PMCID: PMC9636888
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2022.05.006
Necroptosis in heart disease: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications
Abstract
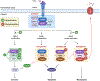
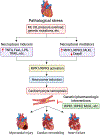
Cell death is a crucial event underlying cardiac ischemic injury, pathological remodeling, and heart failure. Unlike apoptosis, necrosis had long been regarded as a passive and unregulated process. However, recent studies demonstrate that a significant subset of necrotic cell death is actively mediated through regulated pathways - a process known as "regulated necrosis". As a form of regulated necrosis, necroptosis is mediated by death receptors and executed through the activation of receptor interacting protein kinase 3 (RIPK3) and its downstream substrate mixed lineage kinase-like domain (MLKL). Recent studies have provided compelling evidence that necroptosis plays an important role in myocardial homeostasis, ischemic injury, pathological remodeling, and heart failure. Moreover, it has been shown that genetic and pharmacological manipulations of the necroptosis signaling pathway elicit cardioprotective effects. Important progress has also been made regarding the molecular mechanisms that regulate necroptotic cell death in vitro and in vivo. In this review, we discuss molecular and cellular mechanisms of necroptosis, potential crosstalk between necroptosis and other cell death pathways, functional implications of necroptosis in heart disease, and new therapeutic strategies that target necroptosis signaling.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Heart failure; Myocardial infarction; Necroptosis; Necrosis.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Kung G, Konstantinidis K, Kitsis RN, Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, in the heart, Circ. Res 108 (2011) 1017–1036. - PubMed
-
- Whelan RS, Kaplinskiy V, Kitsis RN, Cell death in the pathogenesis of heart disease: mechanisms and significance, Annu. Rev. Physiol 72 (2010) 19–44. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Chua CC, Ho YS, Hamdy RC, Chua BH, Overexpression of Bcl-2 attenuates apoptosis and protects against myocardial I/R injury in transgenic mice, Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol 280 (2001) H2313–H2320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

