mRNA-based therapeutics: powerful and versatile tools to combat diseases
- PMID: 35597779
- PMCID: PMC9123296
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-022-01007-w
mRNA-based therapeutics: powerful and versatile tools to combat diseases
Abstract
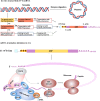
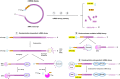
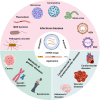
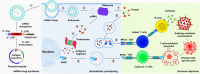
The therapeutic use of messenger RNA (mRNA) has fueled great hope to combat a wide range of incurable diseases. Recent rapid advances in biotechnology and molecular medicine have enabled the production of almost any functional protein/peptide in the human body by introducing mRNA as a vaccine or therapeutic agent. This represents a rising precision medicine field with great promise for preventing and treating many intractable or genetic diseases. In addition, in vitro transcribed mRNA has achieved programmed production, which is more effective, faster in design and production, as well as more flexible and cost-effective than conventional approaches that may offer. Based on these extraordinary advantages, mRNA vaccines have the characteristics of the swiftest response to large-scale outbreaks of infectious diseases, such as the currently devastating pandemic COVID-19. It has always been the scientists' desire to improve the stability, immunogenicity, translation efficiency, and delivery system to achieve efficient and safe delivery of mRNA. Excitingly, these scientific dreams have gradually been realized with the rapid, amazing achievements of molecular biology, RNA technology, vaccinology, and nanotechnology. In this review, we comprehensively describe mRNA-based therapeutics, including their principles, manufacture, application, effects, and shortcomings. We also highlight the importance of mRNA optimization and delivery systems in successful mRNA therapeutics and discuss the key challenges and opportunities in developing these tools into powerful and versatile tools to combat many genetic, infectious, cancer, and other refractory diseases.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest. X.S. and M.W. are members of the editorial board; they have not been involved In the process of the manuscript handling.
Figures




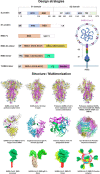
References
-
- Conry RM, et al. Characterization of a messenger RNA polynucleotide vaccine vector. Cancer Res. 1995;55:1397–1400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

