Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and white matter lesions in patients with migraine
- PMID: 35597897
- PMCID: PMC9123779
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-022-02715-0
Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and white matter lesions in patients with migraine
Abstract
Background/aim: White matter lesions (WML) are more frequently observed in migraine patients than in the average population. Associations between Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection and different extraintestinal pathologies have been identified. Here, we aimed to investigate the association between H. pylori infection and WML in patients diagnosed with episodic migraine.
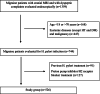
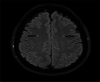
Materials and methods: A retrospective study was conducted with 526 subjects with a diagnosis of episodic migraine. Hyperintensity of WML had been previously evaluated in these patients with brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examinations. Previous endoscopic gastric biopsy histopathological examination of the same patients and reports on H. pylori findings were recorded. The demographic characteristics of the patients, such as age, gender and chronic systemic diseases such as hypertension and diabetes mellitus (DM) were recorded. Statistical evaluation was made.
Results: Evaluation was made among 526 migraine patients who met the inclusion criteria, comprising 397 (75.5%) females and 129 (24.5%) males with a mean age of 45.57 ± 13.46 years (range, 18-69 years). WML was detected on brain MRI in 178 (33.8%) patients who were also positive for H. pylori (p < 0.05). Subjects who are H. pylori-positive with migraine, WML were observed at a 2.5-fold higher incidence on brain MRI (odds ratio: 2.562, 95% CI 1.784-3.680). WML was found to be more significant in patients with hypertension and migraine than those without (p < 0.001). Older age was also found to be associated with WML (OR = 1.07, 95% CI: 0.01-0.04, p < 0.001). The age (p < 0.001), H. pylori (p < 0.001), hypertension (p < 0.001), and hypertension + DM (p < 0.05), had significant associations in predicting WML according to the multivariate logistic regression analysis. The presence of hypertension had a higher odds ratio value than the other variables.
Conclusion: It was concluded that H. pylori infection, as a chronic infection, can be considered a risk factor in developing WML in subjects with migraine.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; Migraine; White matter lesions.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The presence of brain white matter lesions in relation to preeclampsia and migraine.Cephalalgia. 2016 Mar;36(3):284-8. doi: 10.1177/0333102415586065. Epub 2015 May 8. Cephalalgia. 2016. PMID: 25957305
-
[Study of the relationship between white matter lesions in the magnetic resonance imaging and patent foramen ovale].Neurologia. 2008 Oct;23(8):499-502. Neurologia. 2008. PMID: 18770058 Spanish.
-
Is ischemia associated with the formation of White matter lesions in migraine?Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020 Jun;193:105770. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.105770. Epub 2020 Mar 2. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32197144
-
Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and migraine: a meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct 28;20(40):14965-72. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14965. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25356058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is Diabetes Mellitus a Predisposing Factor for Helicobacter pylori Infections?Curr Diab Rep. 2023 Aug;23(8):195-205. doi: 10.1007/s11892-023-01511-5. Epub 2023 May 22. Curr Diab Rep. 2023. PMID: 37213058 Review.
Cited by
-
Helicobacter pylori Infection in Children: A Possible Reason for Headache?Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Mar 29;13(7):1293. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13071293. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046511 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori, persistent infection burden and structural brain imaging markers.Brain Commun. 2024 Mar 13;6(2):fcae088. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcae088. eCollection 2024. Brain Commun. 2024. PMID: 38529358 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoogeveen ES, Arkink EB, van der Grond J, van Buchem MA, Ferrari MD, et al. MRI evaluation of the relationship between carotid artery endothelial shear stress and brain white matter lesions in migraine the. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020;40(5):1040–1047. doi: 10.1177/0271678X19857810. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous