Challenges faced by patients with dyslipidemia and systemic arterial hypertension in Brazil: a design of the patient journey
- PMID: 35597901
- PMCID: PMC9124411
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-022-02669-8
Challenges faced by patients with dyslipidemia and systemic arterial hypertension in Brazil: a design of the patient journey
Abstract
Background and objective: Non-communicable diseases like systemic arterial hypertension (SAH) and dyslipidemia are poorly studied in terms of patient journey aspects. This semi-systematic review provides evidence synthesis for the management of SAH and dyslipidemia in Brazil and also discusses challenges faced by patients at the local level along with a suggested care approach by local experts.
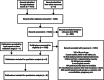
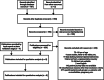
Methods: A semi-systematic review using both structured literature databases (Embase and Medline) and unstructured scientific records (WHO, IPD, MOH and Google) on hypertension and dyslipidemia in the English language from 2010 to 2019 was performed by reviewers. After two-level screening based on pre-defined criteria, patient journey touchpoints and prevalence information were extracted from the included articles. Data gaps were bridged through the insights of local experts.
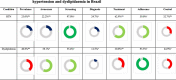
Results: Prevalence of hypertension and dyslipidemia in Brazil were 23% and 40.8%, respectively. Awareness of dyslipidemia was found in a larger proportion (58.1%) than in SAH (22.2%). Similarly, screening for hypertension (97%) and dyslipidemia (55.4%) were found to be effective, while treatment was (62.9%) and (30.0%) for hypertension and dyslipidemia, respectively.
Conclusion: There were important gaps on patient awareness and treatment of dyslipidemia and hypertension. Limited patient education, regional disease distribution, and treatment allocation, along with limited resources for diagnosis and treatment are the key challenges.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Dyslipidemia; Patient journey; Prevalence; Systemic arterial hypertension; Treatment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
JRF received honoraria for consulting, speaker, or research activities from Aché, Astra Zeneca, Amgen, EMS, Merck, MSD, Novo-Nordisk, Pfizer, PTC therapeutics, and Sanofi/Regeneron. He is a recipient of a scholarship from the Conselho Nacional de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento Tecnologico (CNPq) process # 314145/2018-4. RDS received honoraria for consulting, speaker, or research activities from Abbott, Aché, Astra Zeneca, Amgen, EMS, Esperion, GETZ pharma, Kowa, Libbs, Merck, MSD, Novo-Nordisk, Novartis, Pfizer, PTC Therapeutics, Roche and Sanofi/Regeneron. He is a recipient of a scholarship from the Conselho Nacional de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento Tecnologico (CNPq) process # 303734/2018-3, Brazil. LFV, ENS and CRY are employees of Pfizer Upjohn.
Figures

References
-
- Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases...). Accessed 29 Jan 2021.
-
- Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, Danaei G, Shibuya K, Adair-Rohani H, et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2224–2260. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61766-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

