Identification of excretory and secretory proteins from Haemonchus contortus inducing a Th9 immune response in goats
- PMID: 35597967
- PMCID: PMC9123704
- DOI: 10.1186/s13567-022-01055-8
Identification of excretory and secretory proteins from Haemonchus contortus inducing a Th9 immune response in goats
Abstract
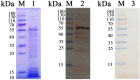
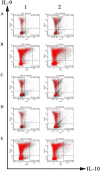
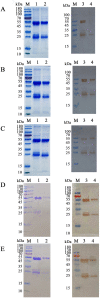
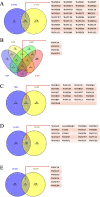
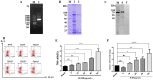
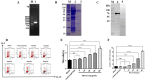
Th9 cells have been shown to play crucial roles in anti-parasite immunity, pathogenic microbe infection, and allergy. Previous studies have demonstrated that Haemonchus contortus excretory and secretory proteins (HcESPs) induce the proliferation of Th9 cells and alter the transcriptional level of IL-9 as well as its related pathways in the Th9 immune response after infection. However, the exact molecule(s) in HcESPs inducing the Th9 immune response is not yet known. In this study, flow cytometry, co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) and shotgun liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) were used, and a total of 218 proteins from HcESPs that might interact with goat Th9 cells were identified. By in vitro culture of Th9 cells with HcESPs, 40 binding proteins were identified. In vivo, 38, 47, 42 and 142 binding proteins were identified at 7, 15, 35 and 50 days post-infection (dpi), respectively. Furthermore, 2 of the 218 HcESPs, named DNA/RNA helicase domain containing protein (HcDR) and GATA transcription factor (HcGATA), were confirmed to induce the proliferation of Th9 cells and promote the expression of IL-9 when incubated with goat peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). This study represents a proteomics-guided investigation of the interactions between Th9 cells and HcESPs. It provides a new way to explore immunostimulatory antigens among HcESPs and identifies candidates for immune-mediated prevention of H. contortus infection.
Keywords: Haemonchus contortus; HcDR; HcGATA; Th9 immune response; binding molecules; proteomics.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kaplan RM, Vidyashankar AN. An inconvenient truth: global worming and anthelmintic resistance. Vet Parasitol. 2012;186:70–78. - PubMed
-
- Geurden T, Chartier C, Fanke J, di Regalbono AF, Traversa D, von Samson-Himmelstjerna G, Demeler J, Vanimisetti HB, Bartram DJ, Denwood MJ. Anthelmintic resistance to ivermectin and moxidectin in gastrointestinal nematodes of cattle in Europe. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2015;5:163–1714. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hu Y, Cheng H. Health risk from veterinary antimicrobial use in China’s food animal production and its reduction. Environ Pollut. 2016;219:993–997. - PubMed
-
- Nisbet AJ, Meeusen EN, González JF, Piedrafita DM. Immunity to Haemonchus contortus and vaccine development. Adv Parasitol. 2016;93:353–396. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

