SMD-YOLO: An efficient and lightweight detection method for mask wearing status during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 35598435
- PMCID: PMC9098810
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.106888
SMD-YOLO: An efficient and lightweight detection method for mask wearing status during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
Background and objective: At present, the COVID-19 epidemic is still spreading worldwide and wearing a mask in public areas is an effective way to prevent the spread of the respiratory virus. Although there are many deep learning methods used for detecting the face masks, there are few lightweight detectors having a good effect on small or medium-size face masks detection in the complicated environments.
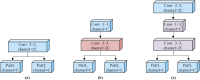
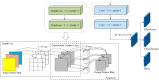
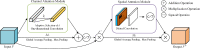
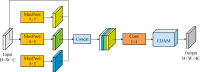
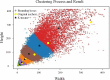
Methods: In this work we propose an efficient and lightweight detection method based on YOLOv4-tiny, and a face mask detection and monitoring system for mask wearing status. Two feasible improvement strategies, network structure optimization and K-means++ clustering algorithm, are utilized for improving the detection accuracy on the premise of ensuring the real-time face masks recognition. Particularly, the improved residual module and cross fusion module are designed to aim at extracting the features of small or medium-size targets effectively. Moreover, the enhanced dual attention mechanism and the improved spatial pyramid pooling module are employed for merging sufficiently the deep and shallow semantic information and expanding the receptive field. Afterwards, the detection accuracy is compensated through the combination of activation functions. Finally, the depthwise separable convolution module is used to reduce the quantity of parameters and improve the detection efficiency. Our proposed detector is evaluated on a public face mask dataset, and an ablation experiment is also provided to verify the effectiveness of our proposed model, which is compared with the state-of-the-art (SOTA) models as well.
Results: Our proposed detector increases the AP (average precision) values in each category of the public face mask dataset compared with the original YOLOv4-tiny. The mAP (mean average precision) is improved by 4.56% and the speed reaches 92.81 FPS. Meanwhile, the quantity of parameters and the FLOPs (floating-point operations) are reduced by 1/3, 16.48%, respectively.
Conclusions: The proposed detector achieves better overall detection performance compared with other SOTA detectors for real-time mask detection, demonstrated the superiority with both theoretical value and practical significance. The developed system also brings greater flexibility to the application of face mask detection in hospitals, campuses, communities, etc.
Keywords: COVID-19; Computer vision; Face mask detection; Object detection; YOLO.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interests The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures









References
-
- Cheng V.C.-C., Wong S.-.C., Chuang V.W.-M., So S.Y.-C., Chen J.H.-K., Sridhar S., To K.K.-W., Chan J.F.-W., Hung I.F.-N., Ho P.-.L., Yuen K.-.Y. The role of community-wide wearing of face mask for control of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) epidemic due to SARS-CoV-2. J. Infect. 2020;81:107–114. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

