Heterologous ChAdOx1 and Bnt162b2 vaccination induces strong neutralizing antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 including delta variant with tolerable reactogenicity
- PMID: 35598855
- PMCID: PMC9117169
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmi.2022.04.019
Heterologous ChAdOx1 and Bnt162b2 vaccination induces strong neutralizing antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 including delta variant with tolerable reactogenicity
Abstract
Objectives: We assessed humoral responses and reactogenicity following the heterologous vaccination compared to the homologous vaccination groups.
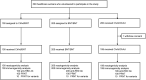
Methods: We enrolled healthcare workers (HCWs) who were either vaccinated with ChAdOx1 followed by BNT162b2 (heterologous group) or 2 doses of ChAdOx1 (ChAdOx1 group) or BNT162b2 (BNT162b2 group). Immunogenicity was assessed by measuring antibody titers against receptor-binding domain (RBD) of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in all participants and neutralizing antibody titer in 100 participants per group. Reactogenicity was evaluated by a questionnaire-based survey.
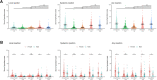
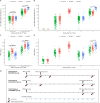
Results: We enrolled 499 HCWs (ChAdOx1, n = 199; BNT162b2, n = 200; heterologous ChAdOx1/BNT162b2, n = 100). The geometric mean titer of anti-receptor-binding domain antibody at 14 days after the booster dose was significantly higher in the heterologous group (11 780.55 binding antibody unit (BAU)/mL [95% CI, 10 891.52-12 742.14]) than in the ChAdOx1 (1561.51 [95% CI, 1415.03-1723.15]) or BNT162b2 (2895.90 [95% CI, 2664.01-3147.98]) groups (both p < 0.001). The neutralizing antibody titer of the heterologous group (geometric mean ND50, 2367.74 [95% CI, 1970.03-2845.74]) was comparable to that of the BNT162b2 group (2118.63 [95% CI, 1755.88-2556.32]; p > 0.05) but higher than that of the ChAdOx1 group (391.77 [95% CI, 326.16-470.59]; p < 0.001). Compared with those against wild-type SARS-CoV-2, the geometric mean neutralizing antibody titers against the Delta variant at 14 days after the boosting were reduced by 3.0-fold in the heterologous group (geometric mean ND50, 872.01 [95% CI, 685.33-1109.54]), 4.0-fold in the BNT162b2 group (337.93 [95% CI, 262.78-434.57]), and 3.2-fold in the ChAdOx1 group (206.61 [95% CI, 144.05-296.34]). The local or systemic reactogenicity after the booster dose in the heterologous group was higher than that of the ChAdOx1 group but comparable to that of the BNT162b2 group.
Discussion: Heterologous ChAdOx1 followed by BNT162b2 vaccination with a 12-week interval induced a robust humoral immune response against SARS-CoV-2, including the Delta variant, that was comparable to the homologous BNT162b2 vaccination and stronger than the homologous ChAdOx1 vaccination, with a tolerable reactogenicity profile.
Keywords: BNT162b2; COVID-19; ChAdOx1; Heterologous vaccination; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2022 European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interdependencies of cellular and humoral immune responses in heterologous and homologous SARS-CoV-2 vaccination.Allergy. 2022 Aug;77(8):2381-2392. doi: 10.1111/all.15247. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Allergy. 2022. PMID: 35124800 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity and reactogenicity against the SARS-CoV-2 variants following heterologous primary series involving CoronaVac, ChAdox1 nCov-19 and BNT162b2 plus BNT162b2 booster vaccination: An open-label randomized study in healthy Thai adults.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022 Nov 30;18(6):2091865. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2091865. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022. PMID: 35816053 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety, reactogenicity, and immunogenicity of homologous and heterologous prime-boost immunisation with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BNT162b2: a prospective cohort study.Lancet Respir Med. 2021 Nov;9(11):1255-1265. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00357-X. Epub 2021 Aug 13. Lancet Respir Med. 2021. PMID: 34391547 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Heterologous Immunization with Prime-Boost COVID-19 Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Oct 11;9(10):1163. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9101163. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34696271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
To mix or not to mix? A rapid systematic review of heterologous prime-boost covid-19 vaccination.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2021 Oct;20(10):1211-1220. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2021.1971522. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2021. PMID: 34415818 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clinical Utility of Sero-Immunological Responses Against SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein During Subsequent Prevalence of Wild-Type, Delta Variant, and Omicron Variant.J Korean Med Sci. 2023 Sep 18;38(37):e292. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e292. J Korean Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37724496 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralizing Activity Against SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron Variants Following a Third BNT162b2 Booster Dose According to Three Homologous or Heterologous COVID-19 Vaccination Schedules.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jul 11;12:948014. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.948014. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35899050 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming the age-dependent SARS-CoV-2 vaccine response through hybrid immunity: analysis of humoral and cellular immunity with mass cytometry profiling.Immun Ageing. 2024 Jul 30;21(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12979-024-00454-z. Immun Ageing. 2024. PMID: 39080742 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Activity and Protective Immunity in Different Vaccine Types Using Three Surrogate Virus Neutralization Test Assays and Two Semiquantitative Binding Assays Targeting the Receptor-Binding Domain.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0266922. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02669-22. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36250875 Free PMC article.
-
Augmented humoral and cellular immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 after breakthrough infection in kidney transplant recipients who received 3 doses of coronavirus disease 2019 vaccine.Am J Transplant. 2023 Apr;23(4):565-572. doi: 10.1016/j.ajt.2022.12.022. Epub 2023 Jan 3. Am J Transplant. 2023. PMID: 36739177 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

