[Advances in Treatment of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations]
- PMID: 35599009
- PMCID: PMC9127758
- DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2022.103.01
[Advances in Treatment of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations]
Abstract
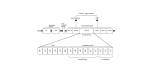
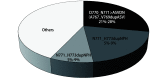
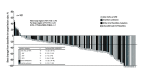
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion mutations are the third most prevalent activating EGFR mutation in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), accounting for 5%-12% of all EGFR mutations in NSCLC cases. Patients harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations exhibit similar clinical characteristics except for worse prognosis as compared to those with 'classic' EGFR mutations. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations are considered as a heterogeneous class of alterations that cause different conformational changes in EGFR. The majority of mutations (almost 90% of cases) is positioned in the loop that immediately follows the C-terminal of the C-helix, and the most widely reported subtype of insertion mutations is D770_N771>ASVDN(A767_V769dupASV) with frequency of 21%-28%. NSCLC patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations show primary drug resistance to previously approved EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors and are generally insensitive to conventional chemotherapy and immunotherapy. The recently approved targeted drugs Amivantamab and Mobocertinib shift the treatment paradigm for NSCLC patients harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. There are also several new compounds targeting NSCLC EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations are in development. In this article, we provide a through overview on the treatment development in EGFR exon 20 insertion mutant NSCLC. .
【中文题目:EGFR外显子20插入突变阳性NSCLC治疗的临床研究进展】 【中文摘要:表皮生长因子受体(epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR)外显子20插入突变是EGFR突变的第三大常见类别,约占所有EGFR突变阳性非小细胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer, NSCLC)的5%-12%。携带EGFR外显子20插入突变的NSCLC患者临床特征与“经典”EGFR激活突变人群相似,但预后很差。EGFR外显子20插入突变异质性高,可导致EGFR不同构象变化。大多数(几乎90%的病例)发生在α-C-螺旋后的Loop环结构区,最常报告的插入突变亚型为D770_N771>ASVDN(A767_V769dupASV),突变频率为21%-28%。目前已知EGFR外显子20插入突变的NSCLC对既往已批准的EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂原发性耐药,而且对传统化疗和免疫治疗也不敏感。近期Amivantamab与Mobocertinib在美国的获批改变了EGFR外显子20插入突变的NSCLC患者的治疗模式。此外,针对NSCLC EGFR外显子20插入突变的其他新型靶向药物正在研发中,期待为该类患者带来更多生存获益。本文就近年来伴有EGFR外显子20插入突变的NSCLC的临床研究进展进行归纳总结,旨在为该类患者的临床治疗提供参考。】 【中文关键词:肺肿瘤;表皮生长因子受体;EGFR外显子20插入突变;靶向治疗】.
Keywords: EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations; Epidermal growth factor receptor; Lung neoplasms; Targeted treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
声明:本文由武田公司提供部分写作支持。作者声明无利益冲突。
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

