Efficacy and safety of mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in lung transplant recipients
- PMID: 35599079
- PMCID: PMC9110371
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jiac.2022.04.019
Efficacy and safety of mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in lung transplant recipients
Abstract
Background: To date, reports addressing the antibody response following mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in lung transplant (LTX) recipients are limited. Thus, the aim of this clinical study was to investigate the efficacy and safety of the vaccines in LTX recipients compared to controls.
Methods: An open-label, nonrandomized prospective study was conducted at Tohoku University Hospital. LTX recipients and controls who received either the BNT162b2 vaccine or the mRNA-1273 vaccine were recruited, and SARS-CoV-2 IgG was measured before and after vaccination. The adverse events were reviewed. Predictors of negative serology after vaccination were evaluated with logistic regression.
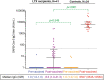
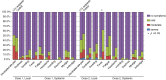
Results: Forty-one LTX recipients and 24 controls were analyzed. Although all controls had a positive antibody response to a SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine, antibody response was found in 24.4% of LTX recipients (p < .0001). The amount of SARS-CoV-2 IgG following the 2nd dose significantly climbed to 6557 AU/mL in controls, whereas the increase in IgG in LTX recipients was 8.3 AU/mL (p < .0001). Fewer LTX recipients developed systemic fever than controls (p < .0001) despite equivalent overall adverse event percentages in both groups. A higher plasma concentration of mycophenolate was a significant predictor of negative serology (p = .032).
Conclusions: An impaired antibody response to mRNA vaccines was significantly found in LTX recipients compared to controls and was associated with the plasma concentration of mycophenolate. While repeating mRNA vaccination may be one of the strategies to improve antibody response given the safety of the vaccines, emerging data on humoral immune responses based on immunosuppression regimens in LTX recipients should be studied (jRCT1021210009).
Keywords: COVID-19; Japan; Lung transplantation; SARS-CoV-2; Vaccine; mRNA.
Copyright © 2022 Japanese Society of Chemotherapy and The Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bergman P., Blennow O., Hansson L., Mielke S., Nowak P., Chen P., et al. Safety and efficacy of the mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 in five groups of immunocompromised patients and healthy controls in a prospective open-label clinical trial. EBioMedicine. 2021;74 doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103705. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

